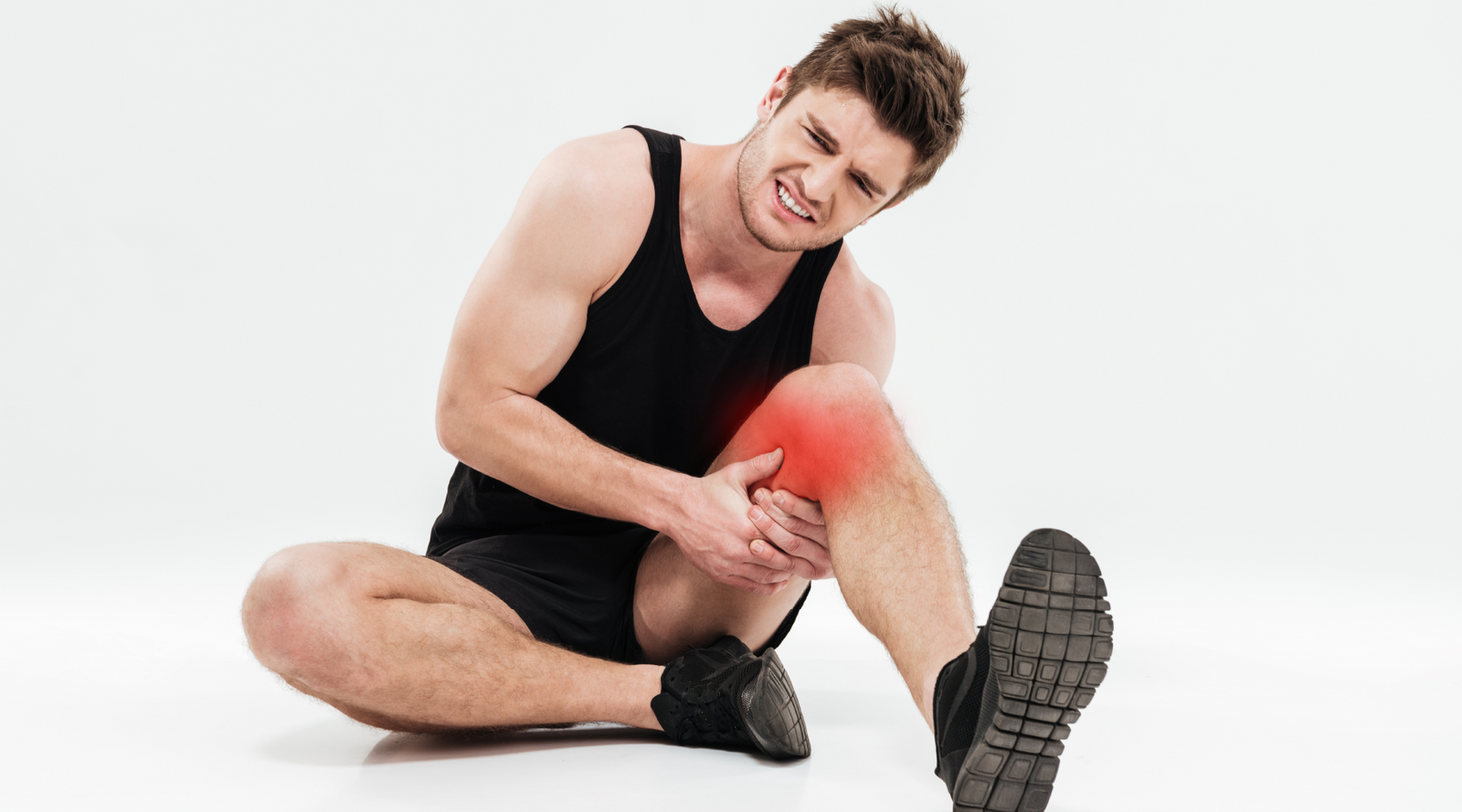
Pain in the side of the knee is a fairly common problem that can interfere with daily activities. It is important to understand the cause so that the correct treatment can be applied. In this answer, we have summarized the most common causes and solutions for pain in the side of the knee.
The most common causes of pain on the side of the knee joint:
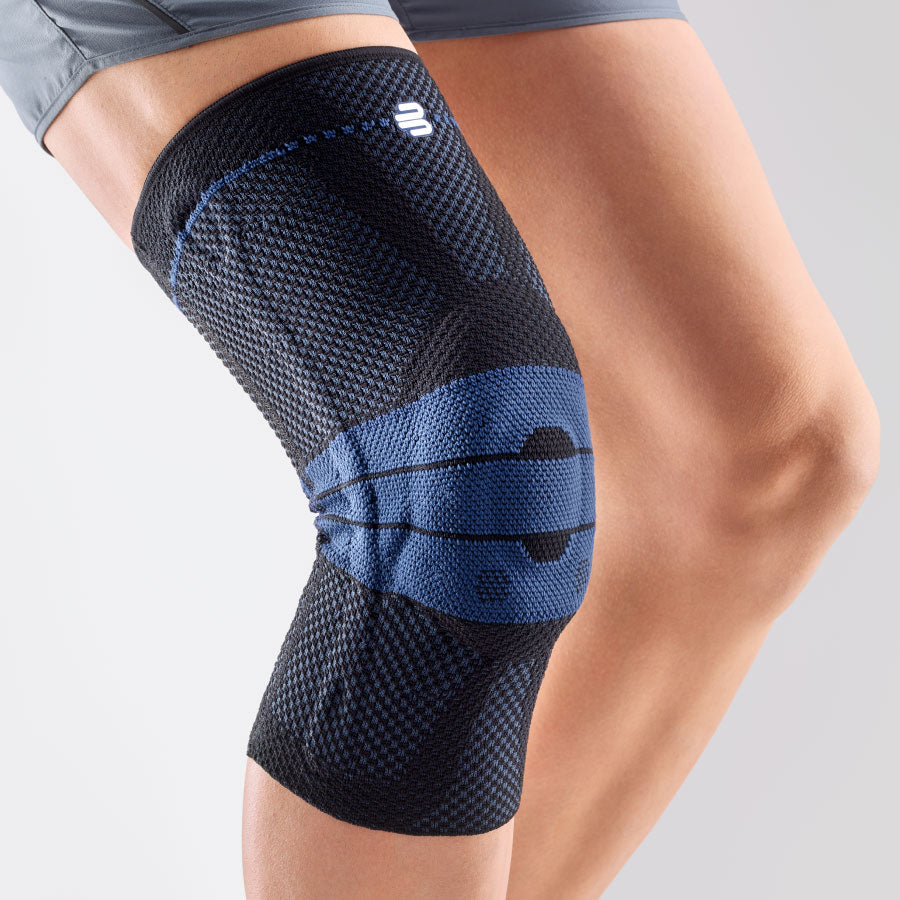
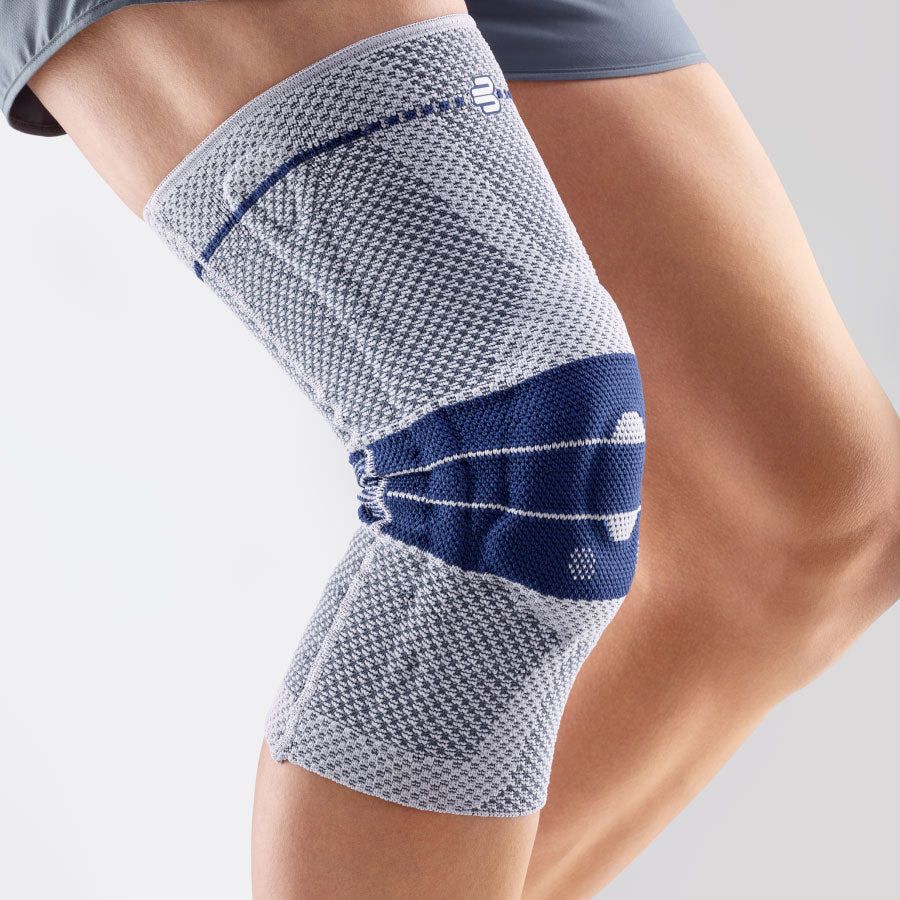
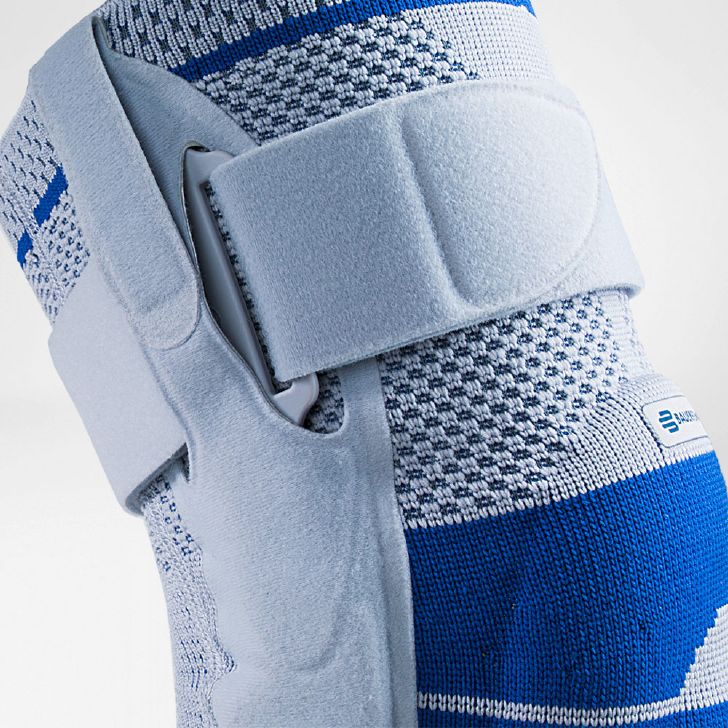
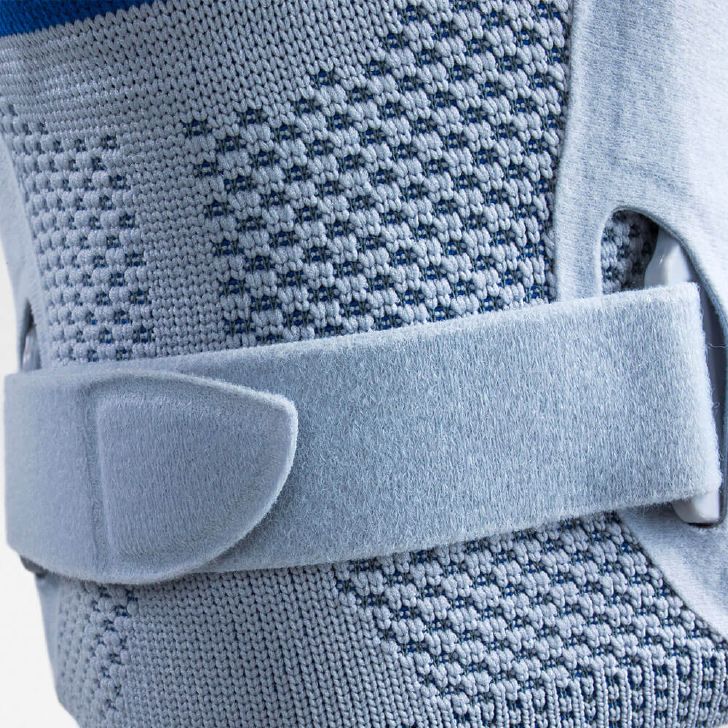
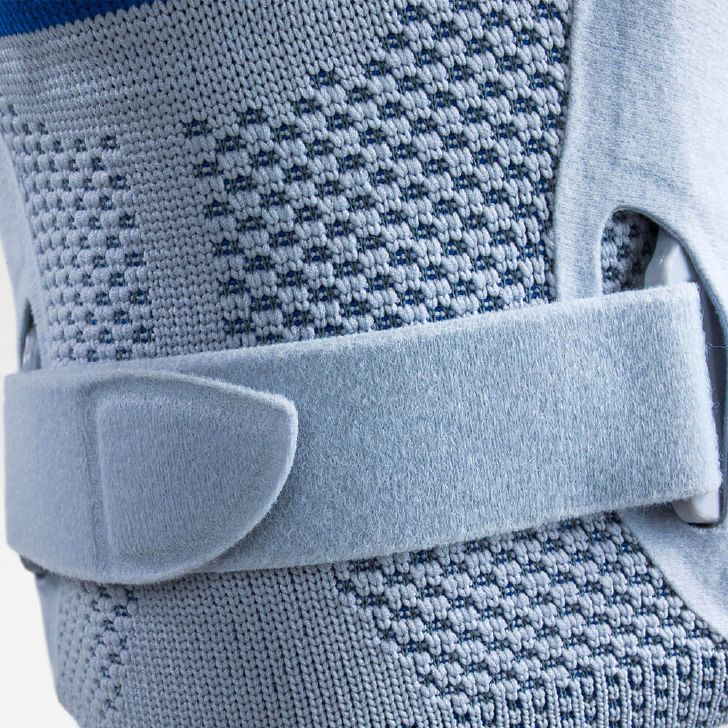
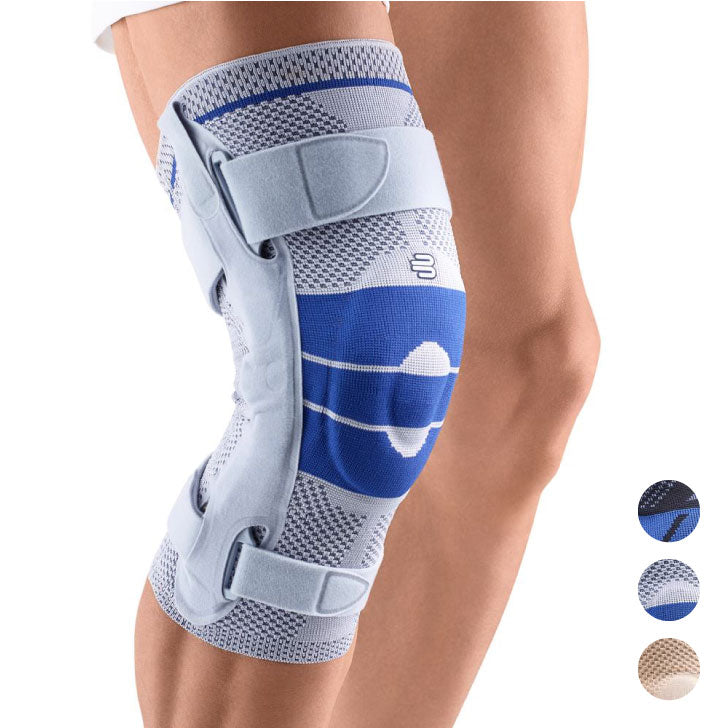
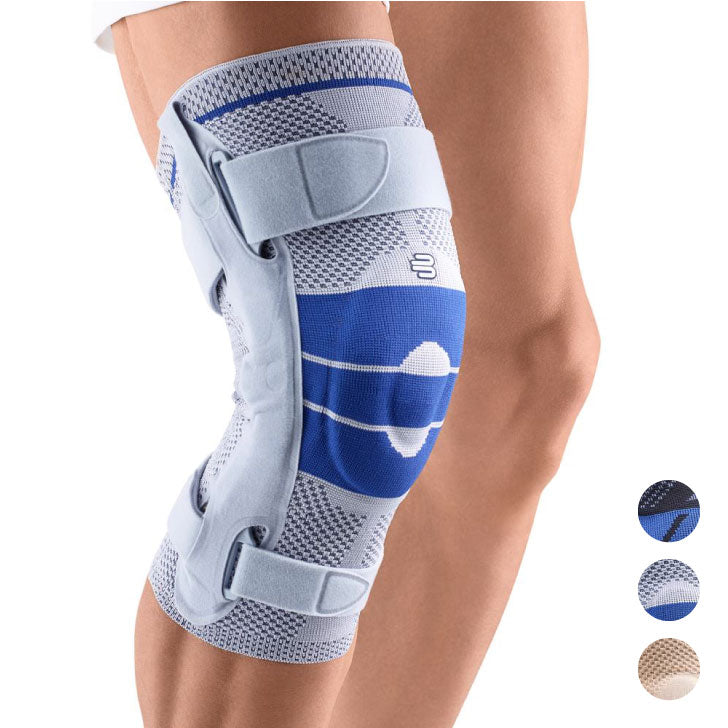
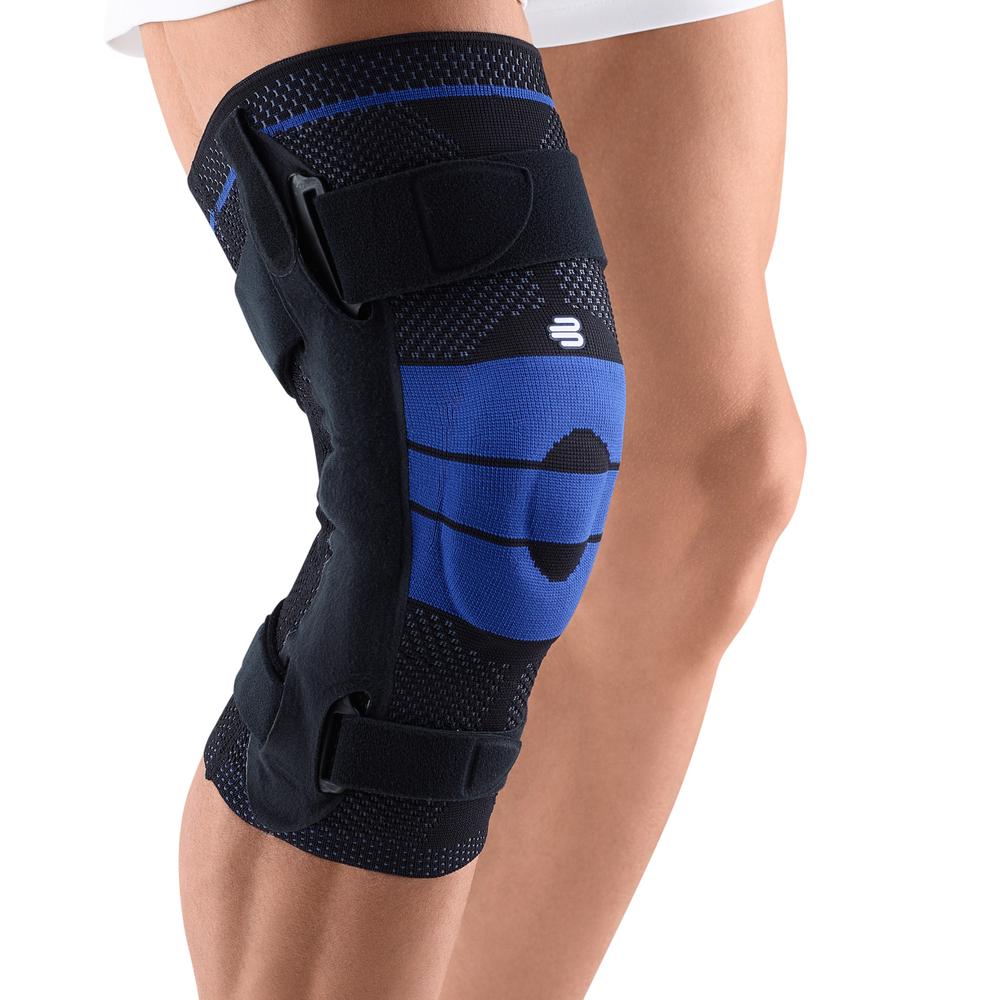
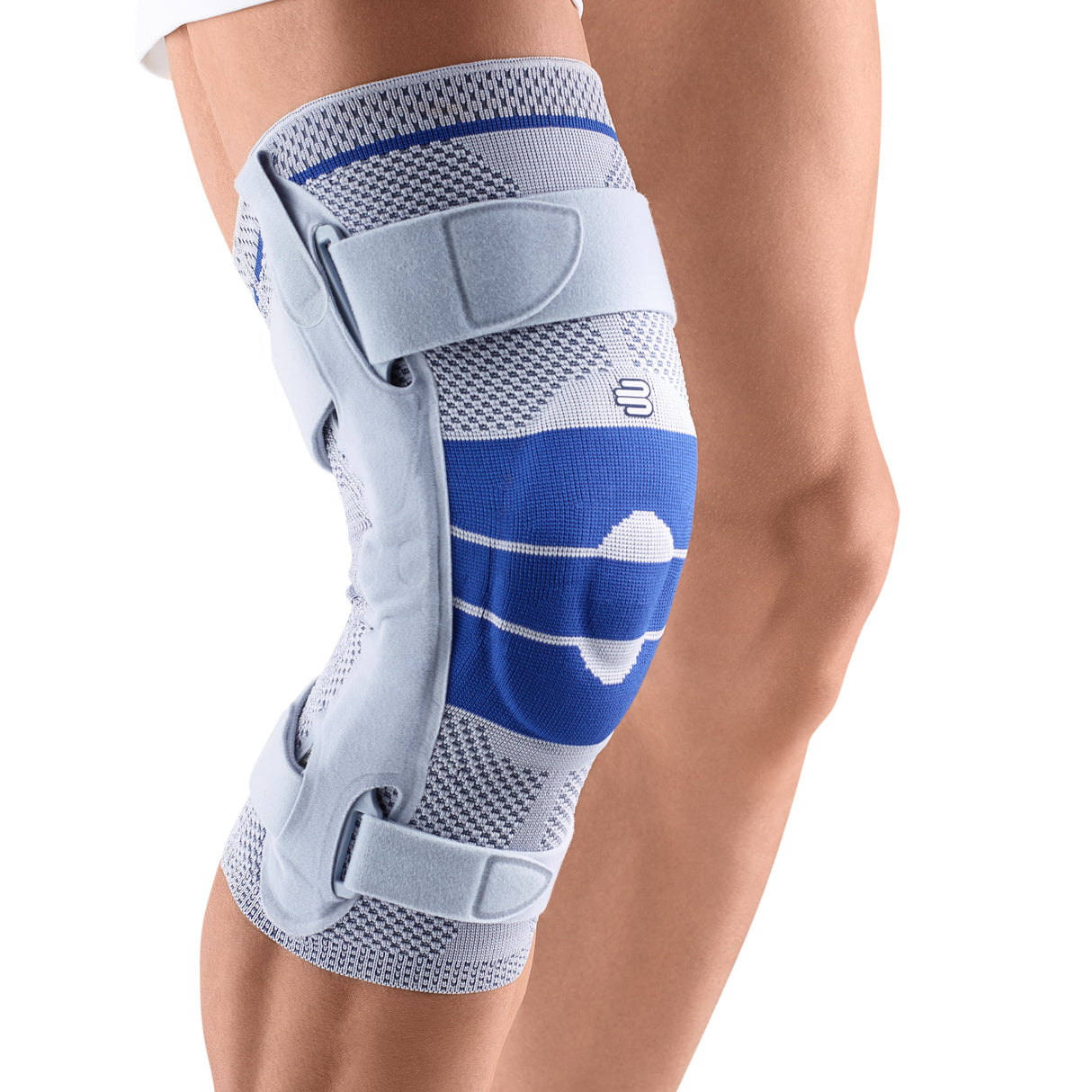
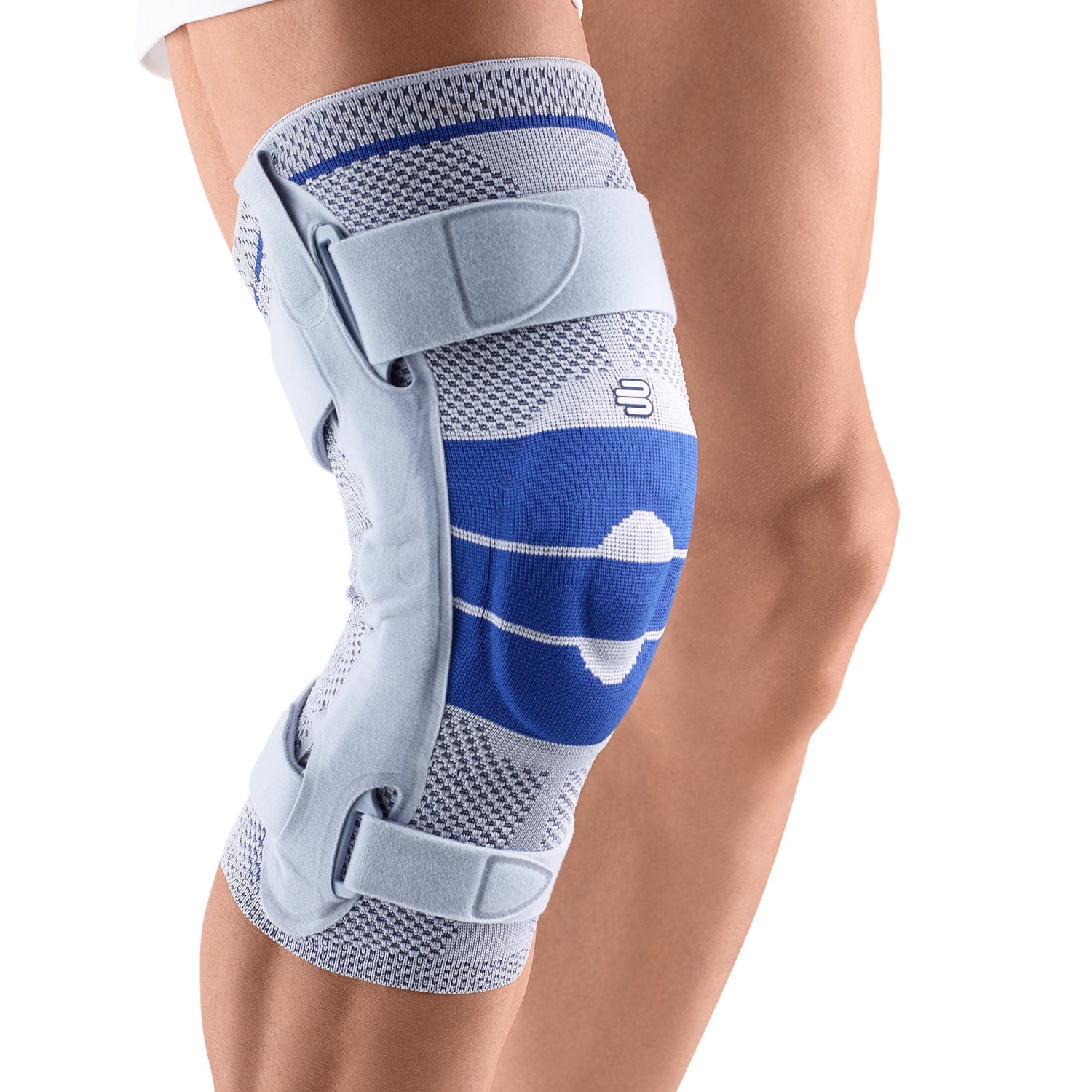
- Lateral ligament injuries (medial and lateral): The knee joint has two main lateral ligaments – the medial (inside) and the lateral (outside). They provide lateral stability. Injuries, such as a sudden turn or a blow to the knee from the side, can cause these ligaments to be sprained or even torn. The pain is usually felt directly at the site of the damaged ligament. The most suitable orthosis GenuTrains S
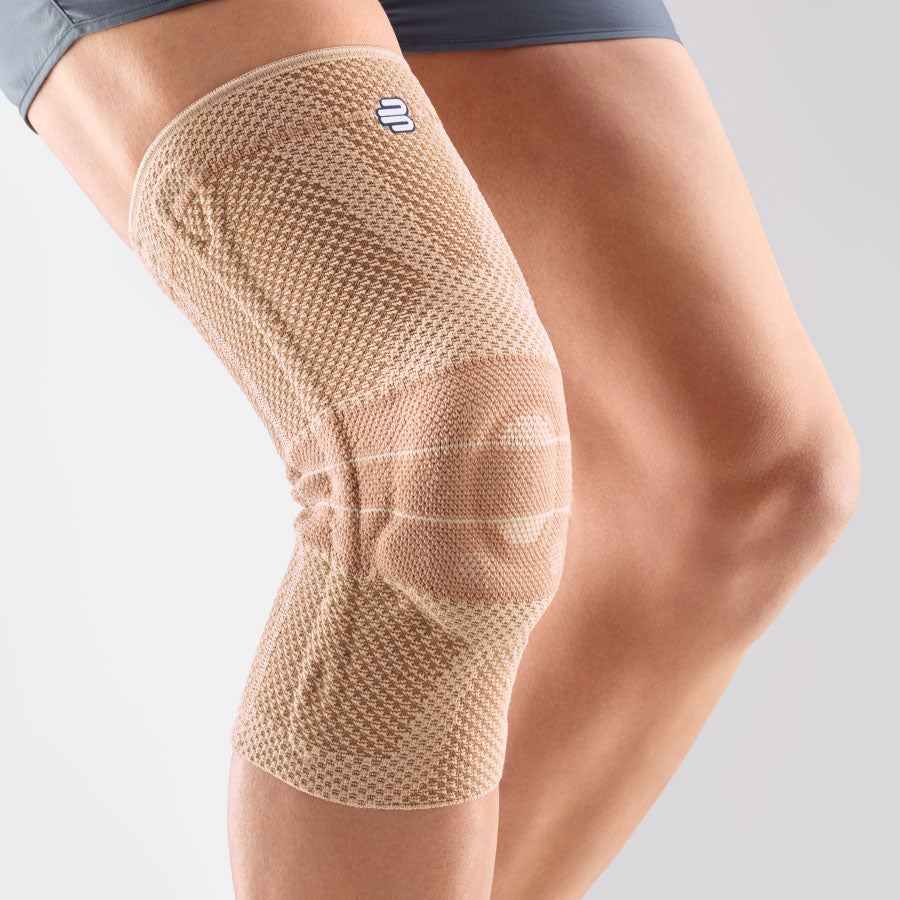
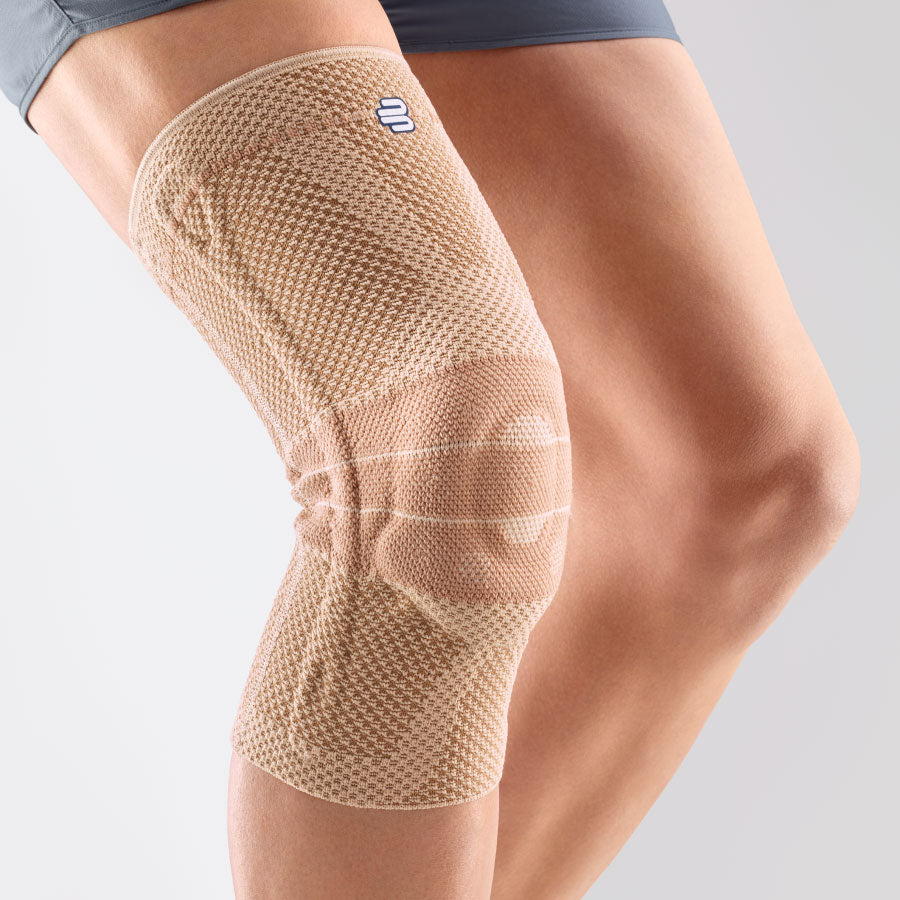
- Meniscus tear: The knee joint has two menisci – the inner (medial) and the outer (lateral) – that act as shock absorbers. A sudden rotation or strong impact can cause a meniscus tear. The pain can be felt both on the side of the knee and deeper in the joint, and it can be worse with certain movements. There may also be a clicking or locking sensation in the knee. The most suitable orthosis GenuTrain
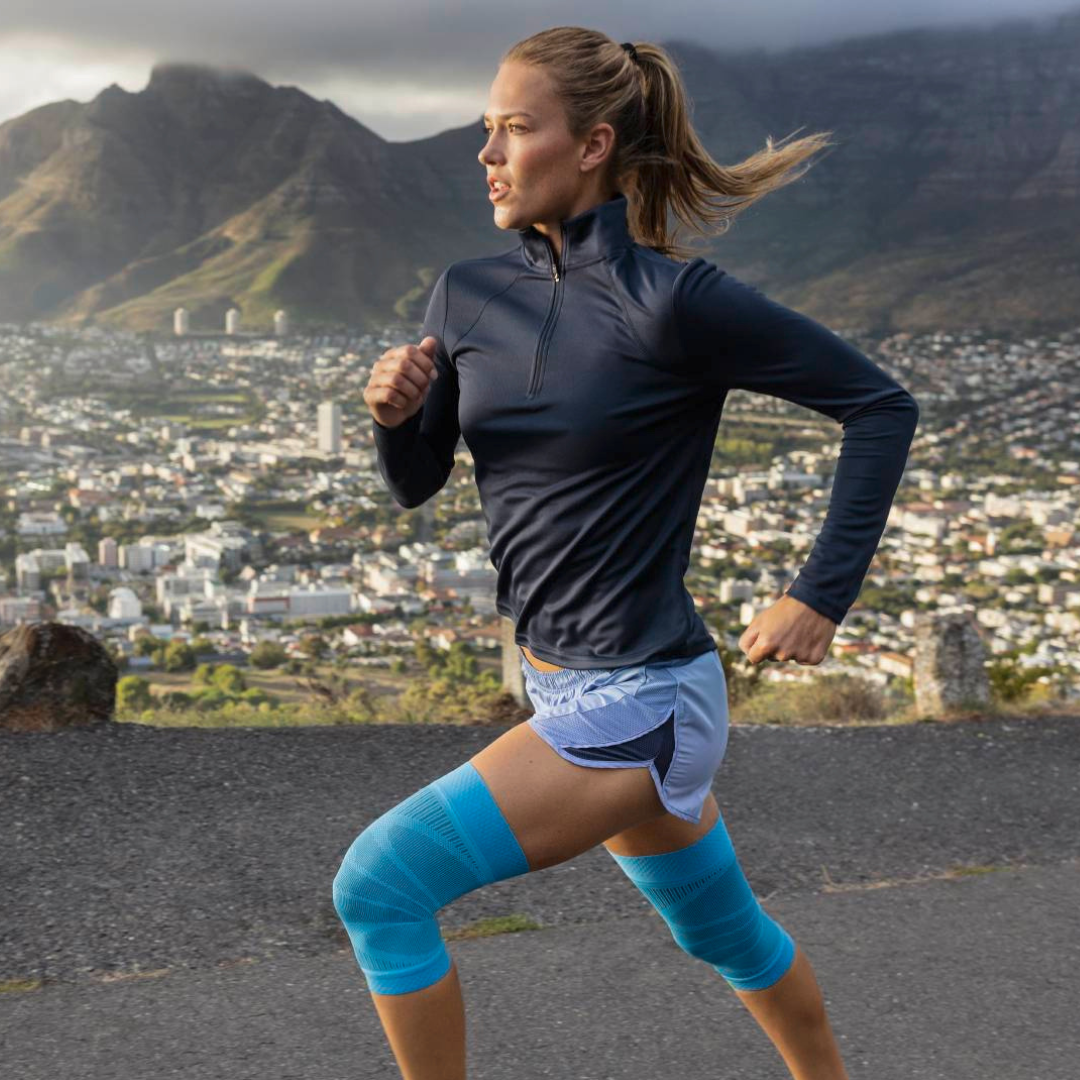
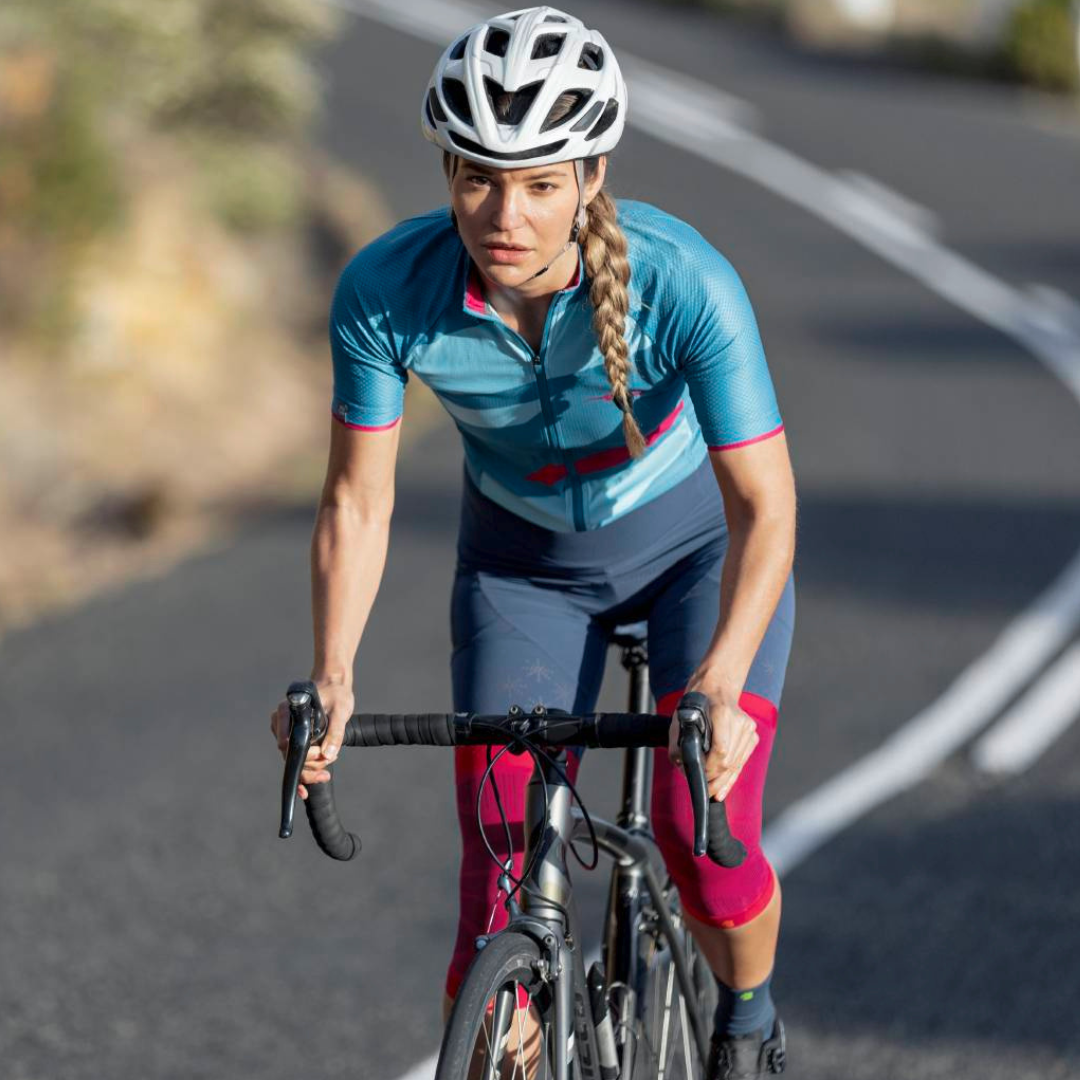
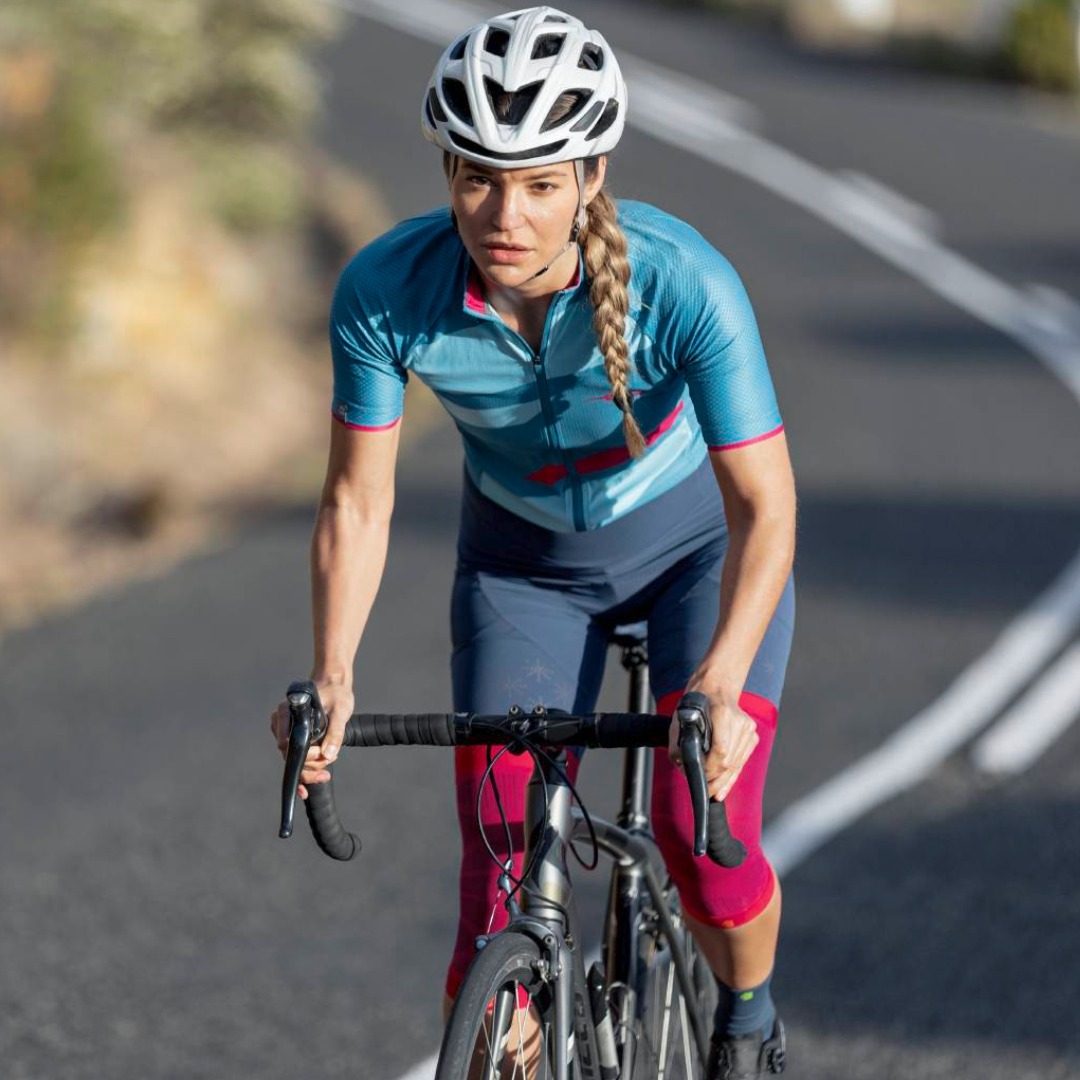
- Iliotibial Band Syndrome (ITBS): This is a condition in which the iliotibial band—a thick band of connective tissue that runs from the hip to the outside of the knee—becomes inflamed or tight. It often occurs in runners and cyclists. The pain is usually felt on the outside of the knee and may worsen during exercise. The best orthosis GenuTrain
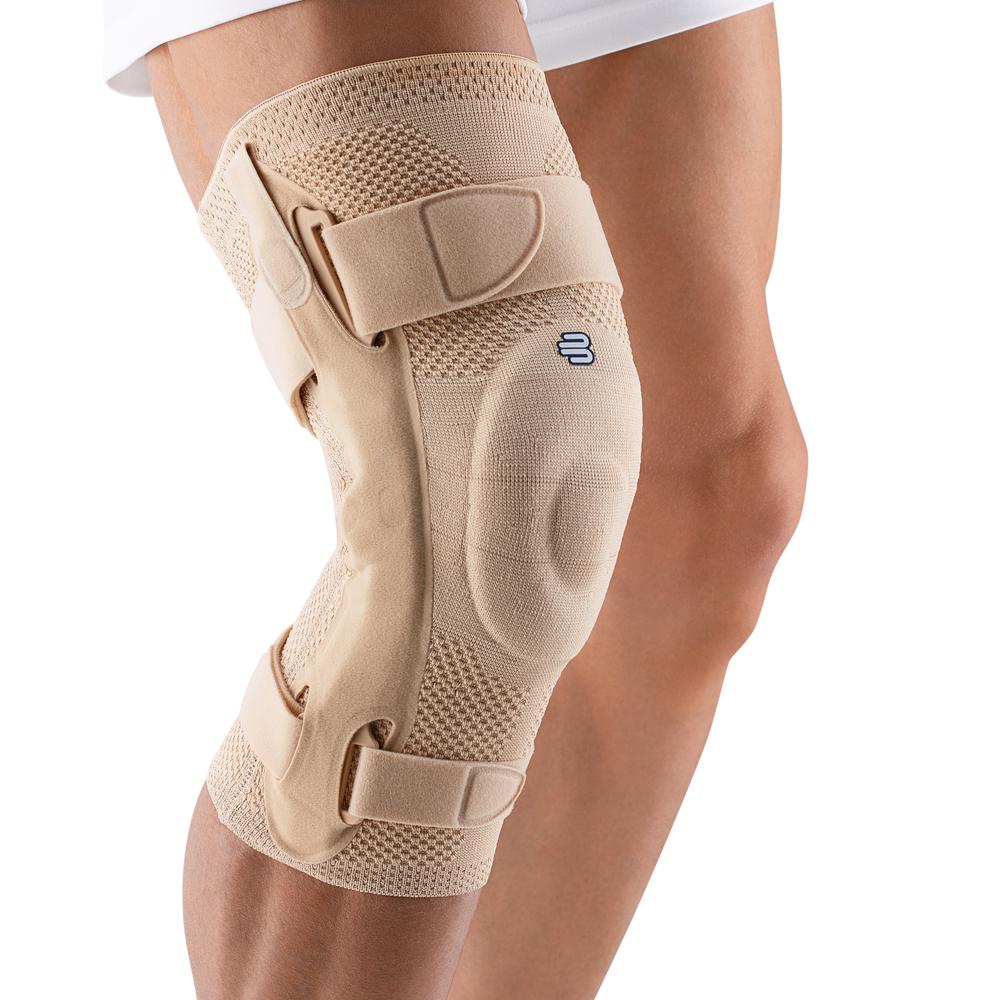
- Osteoarthritis: This is a degenerative joint condition that can also affect the knee joint. The wear and tear of cartilage causes pain, stiffness, and limited mobility. The pain can be felt in the front and sides of the knee. Orthoses for osteoarthritis
- Other less common causes: Sometimes pain in the side of the knee can also be caused by other conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, gout, or other less common conditions.
Solutions for pain relief:
- Rest: If the pain is acute (sudden), it is important to rest the knee and avoid activities that cause pain.
- Ice: Apply ice to the painful area for 15-20 minutes several times a day to reduce inflammation and pain.
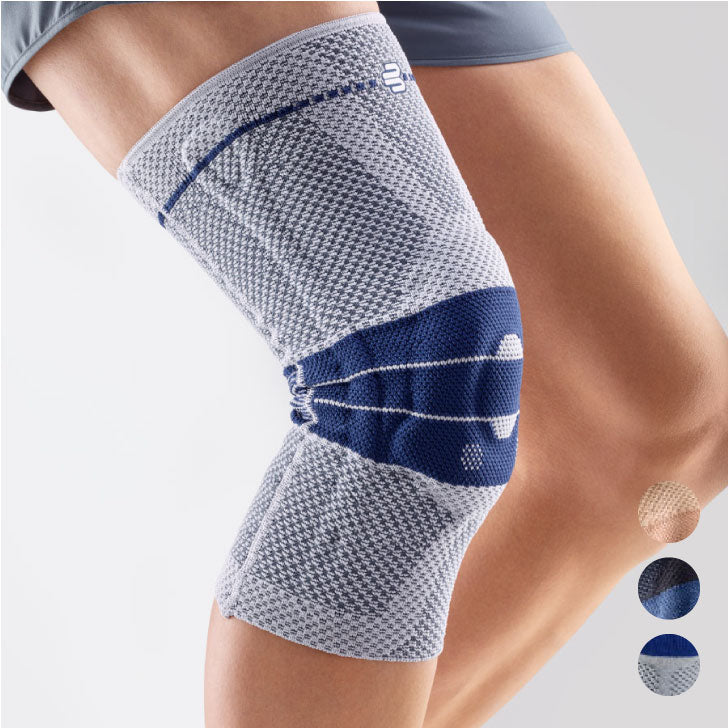
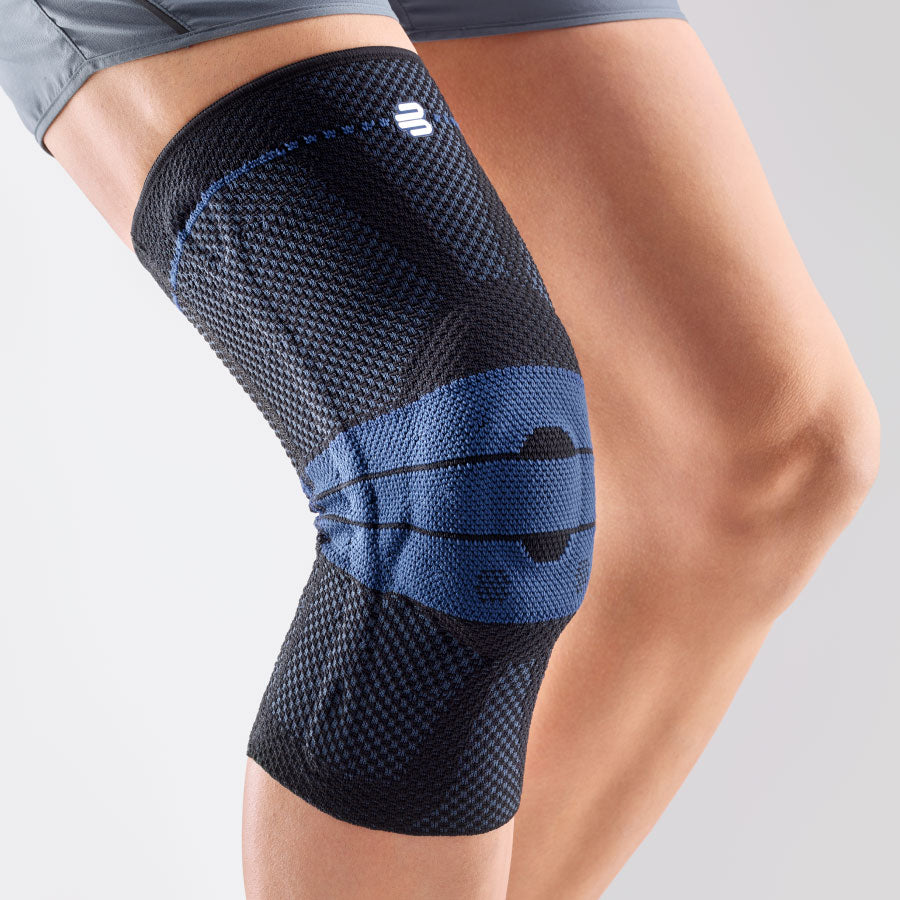
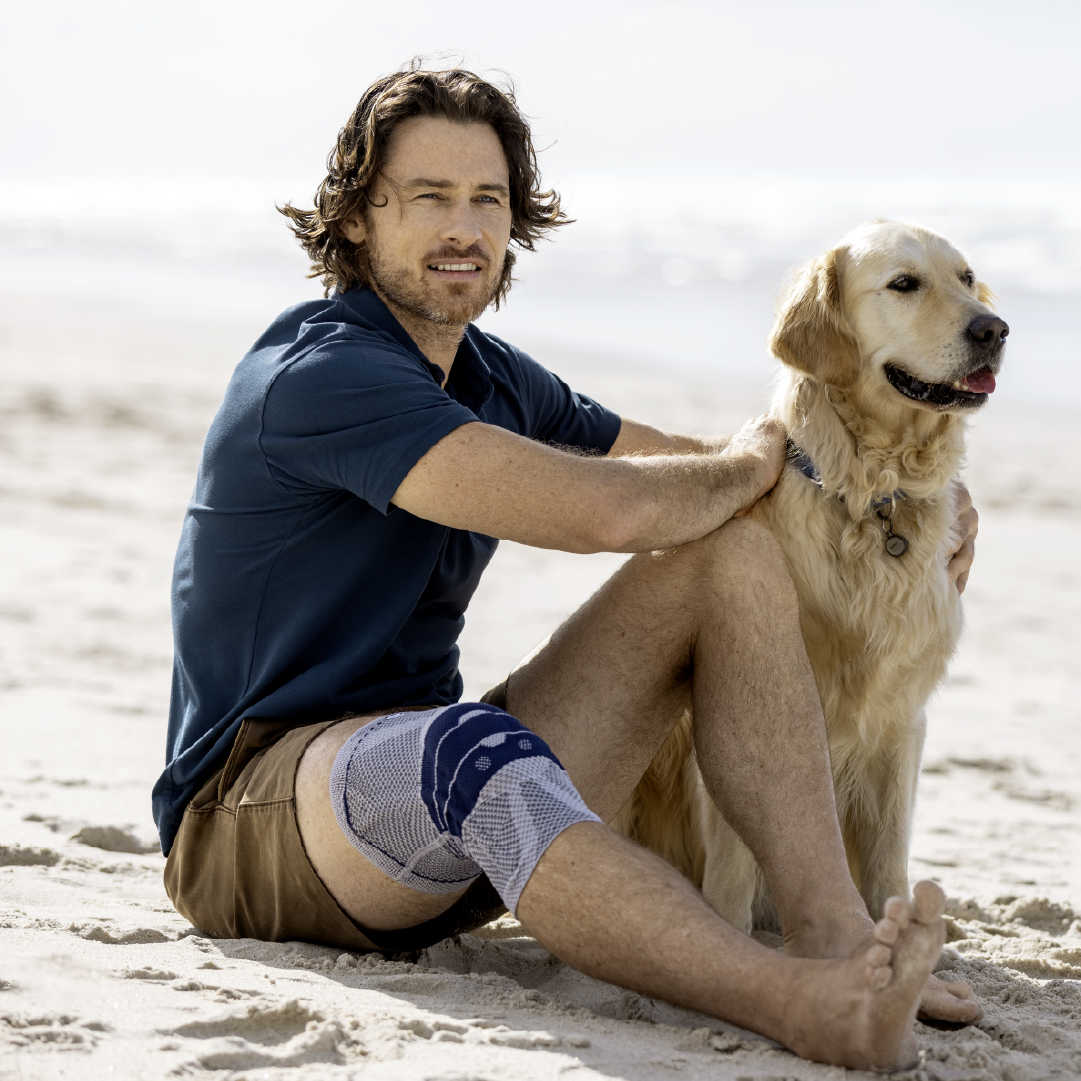
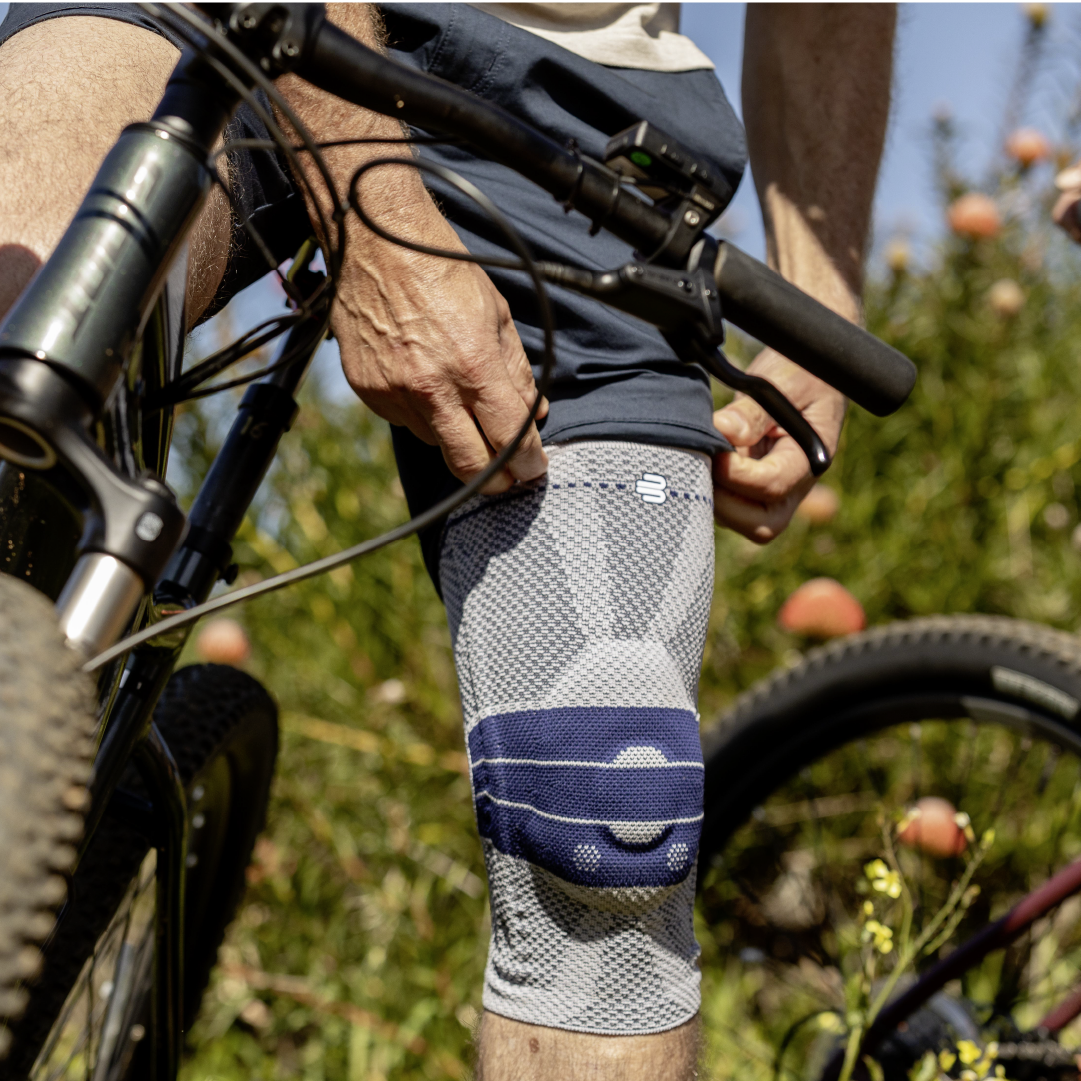
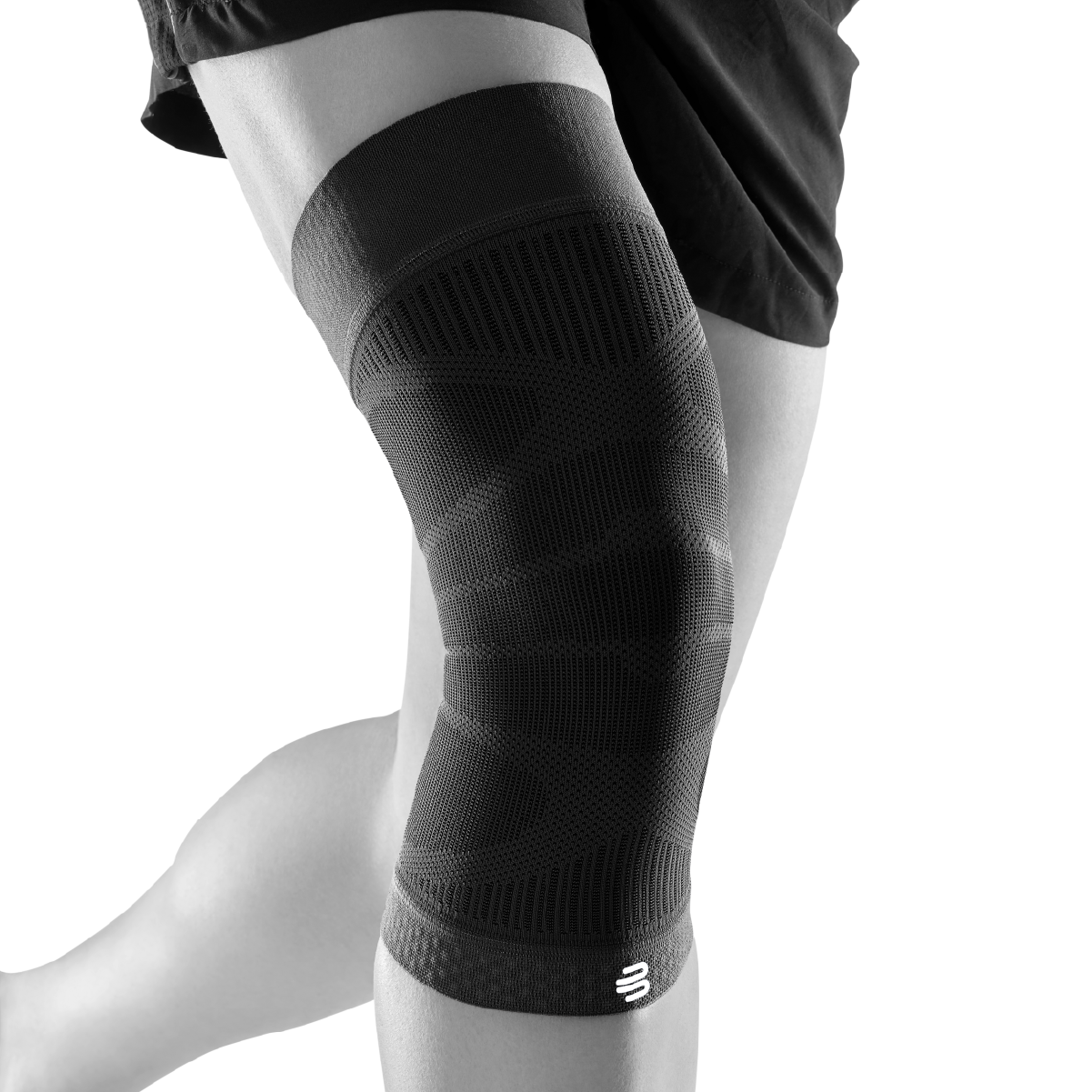
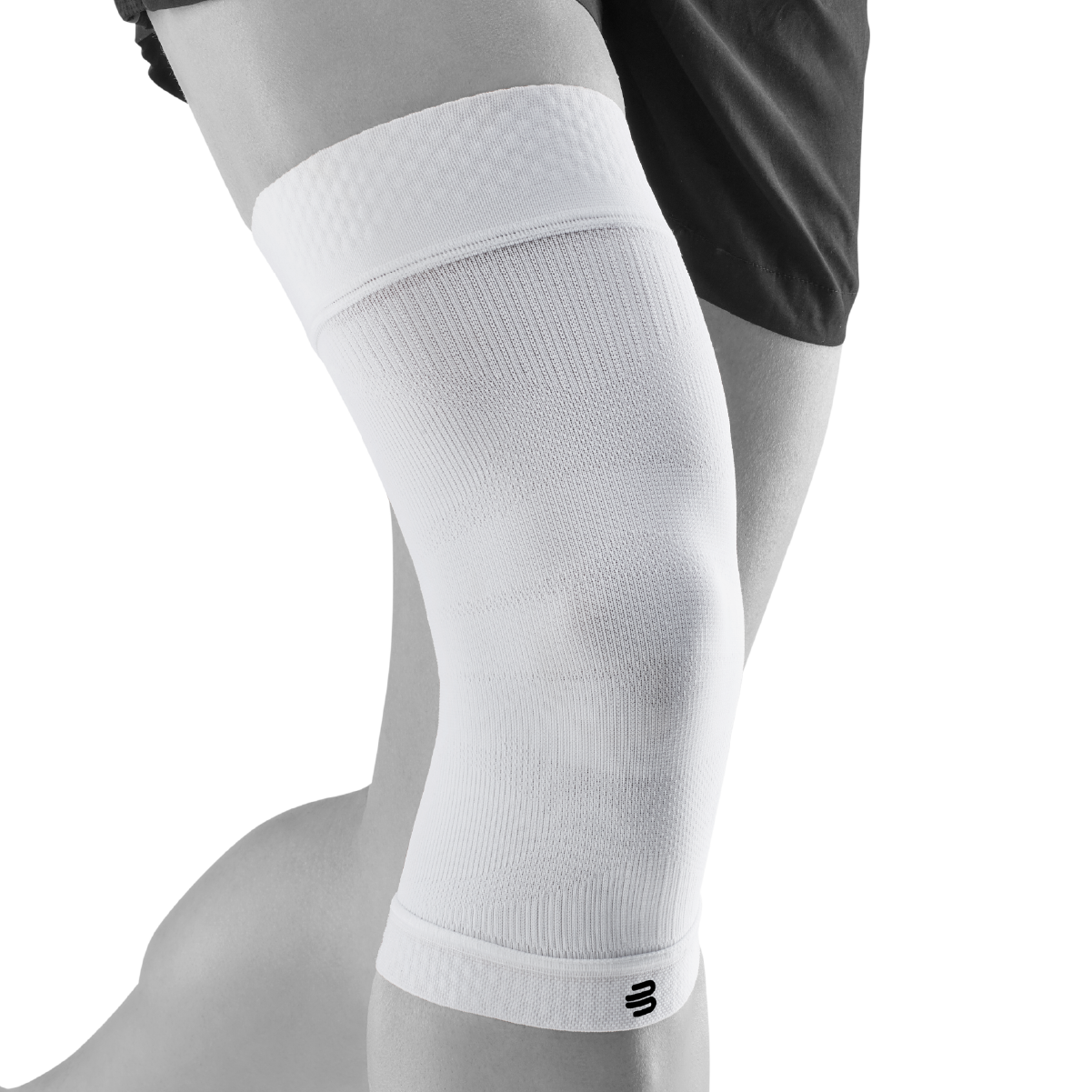
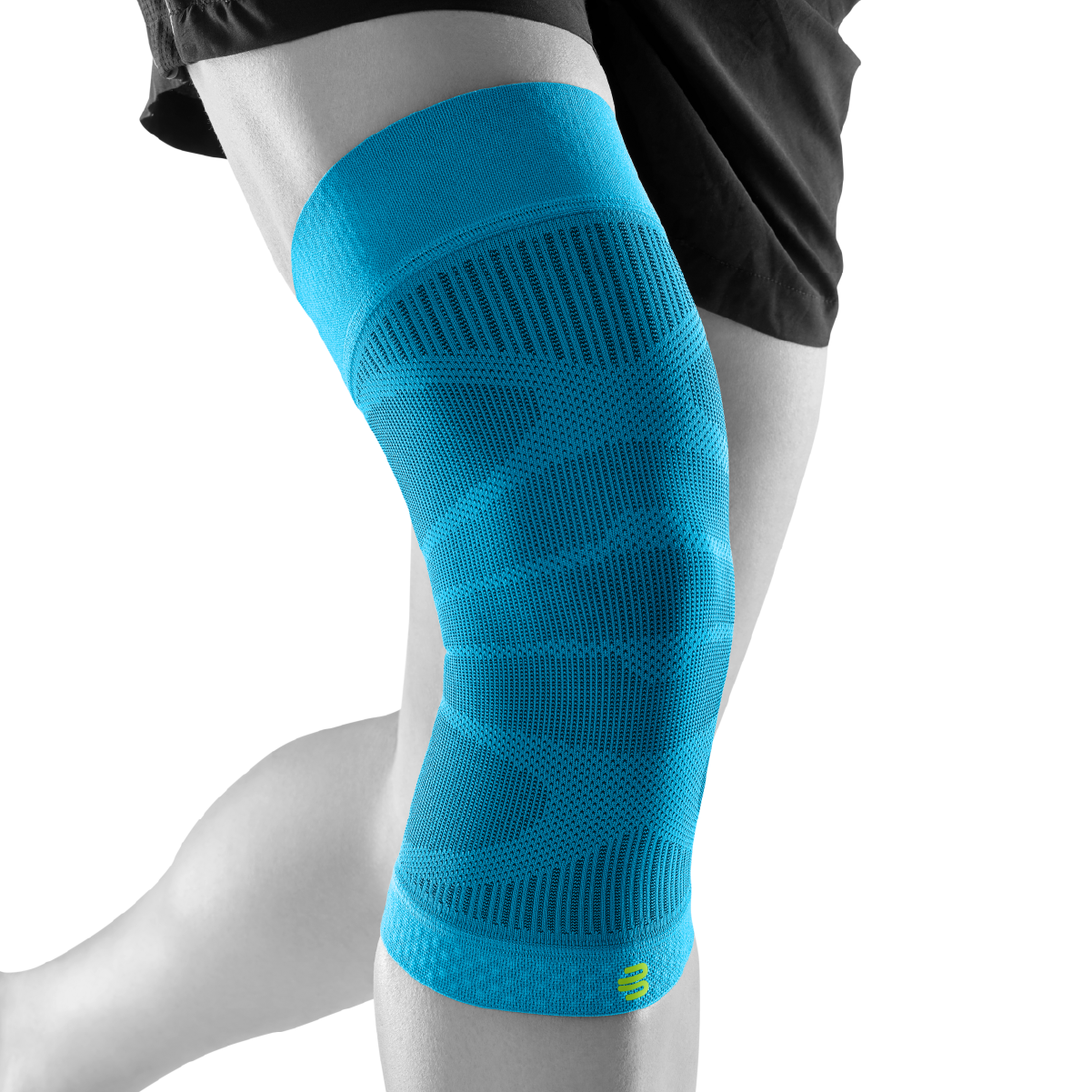
- Compression and knee braces: An elastic bandage or a special knee brace can help stabilize the knee and reduce pain. Bauerfeind knee braces and compression
- Elevation: Keep the painful leg elevated above heart level to reduce swelling.
- Painkillers and anti-inflammatory medications: Over-the-counter medications such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help reduce pain and inflammation. However, check with your doctor or pharmacist before using them.
- Physical therapy: A physical therapist can recommend exercises that strengthen the muscles around the knee and improve joint stability. Strengthening the internal and external platis muscles is especially important.
- Injections (corticosteroids or hyaluronic acid): In more severe cases, your doctor may recommend injections into the knee joint to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Surgical intervention: Surgery may be necessary in cases of severe ligament tears, meniscus damage, or osteoarthritis when other treatments are not effective.
When to see a doctor:
- If the pain is very severe and prevents movement.
- If the knee is swollen or there are visible bruises.
- If there is a feeling of instability in the knee or it "slips".
- If the pain does not go away after a few days of home treatment.
Prevention:
- Wear a knee brace or joint-supporting compression Orthoses and compression for the knee
- Always warm up before physical activity.
- Wear appropriate footwear and use knee support if necessary.
- Strengthen the muscles around your knee with regular exercises.
- Maintain a healthy body weight.
Please note that this information is general and is not a substitute for medical advice. If you are experiencing pain on the side of your knee, please consult a doctor or physical therapist for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.