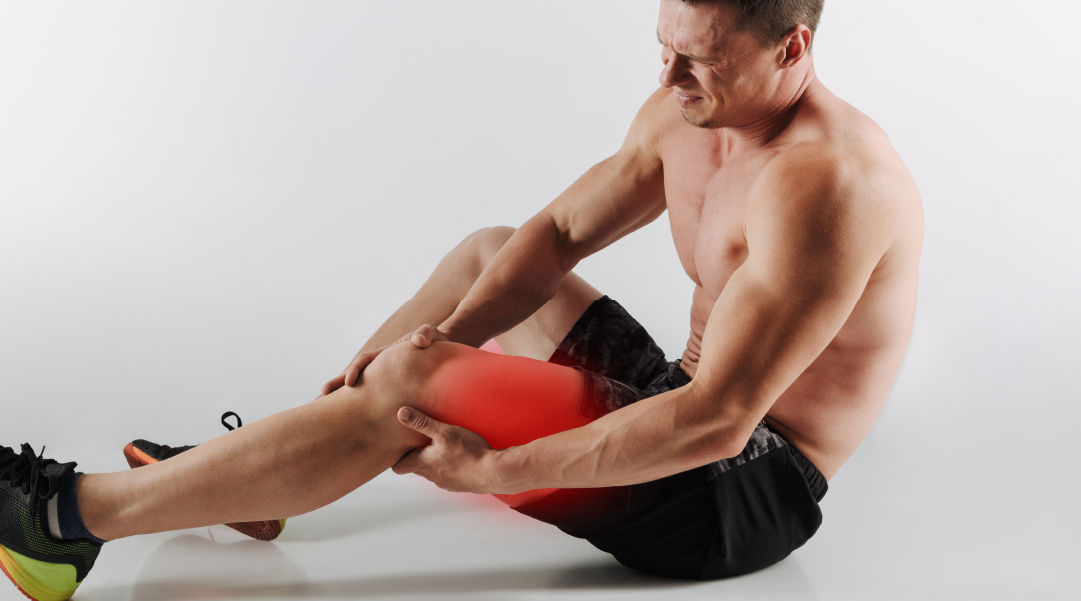
Thigh muscle pain can have a variety of causes, from overuse to more serious medical problems. Here's an overview of the most common causes and possible solutions :
Possible causes of thigh muscle pain
Overload or microtrauma
- Occurs after intense exercise or physical activity (especially running, jumping, or weightlifting).
- Microscopic muscle damage causes inflammation and pain.
Muscle strain or tear
- Sudden pain, often occurring during sports or awkward movements.
- May be associated with a minor or more serious muscle tear.
Sciatica or lumbar nerve compression
- Pain radiating from the back to the thigh (especially the back).
- Often accompanied by tingling or numbness.
Inflammations (myositis, tendonitis)
- Chronic inflammation of muscles or tendons that can develop after injury or overuse.
- It can also be a consequence of autoimmune diseases.
Circulatory disorders
- Pain that occurs during prolonged standing or walking.
- May be related to vein or artery problems (such as peripheral arterial disease).
Other possible causes
- Insufficient fluid intake → muscle cramps.
- Mineral deficiency (e.g. magnesium, potassium deficiency).
- Poor posture or movement biomechanics.
Solutions and recommendations
In the acute phase:
- Rest and cold compresses
- Anti-inflammatory medications (such as ibuprofen)
- Light stretching and resuming movement gradually
Long-term solutions and prevention:
- Warming up and stretching muscles before exercise
- Specific exercises for strengthening the thighs
- Adequate water and electrolyte intake
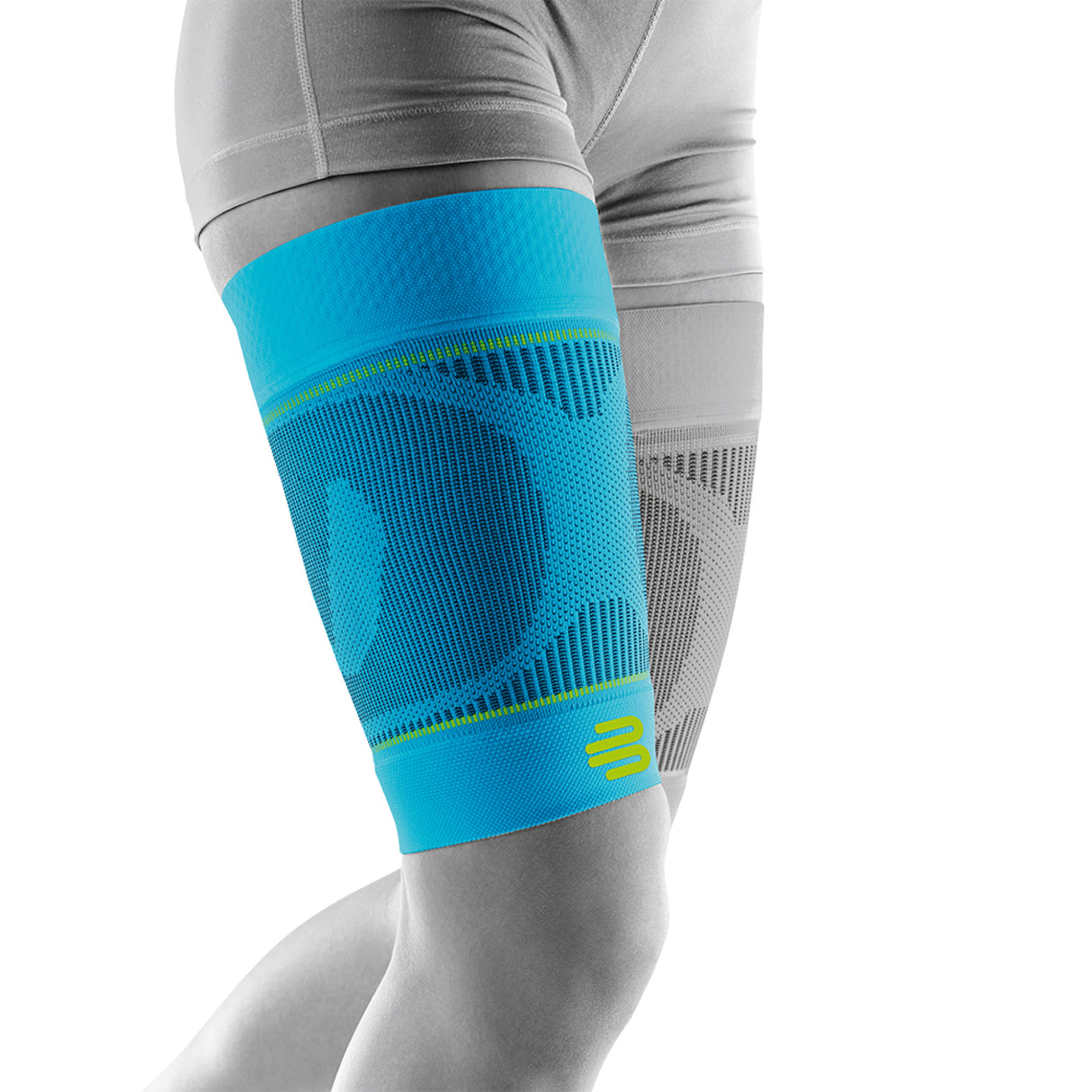
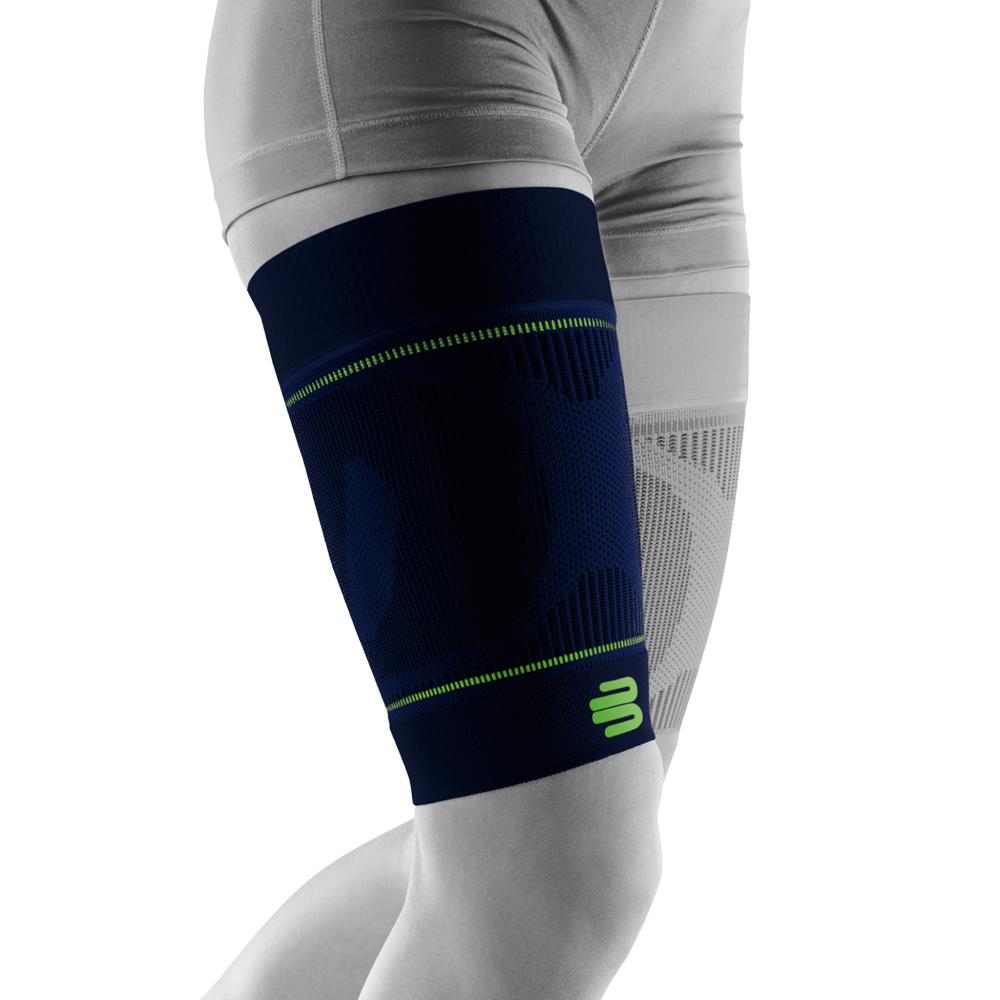
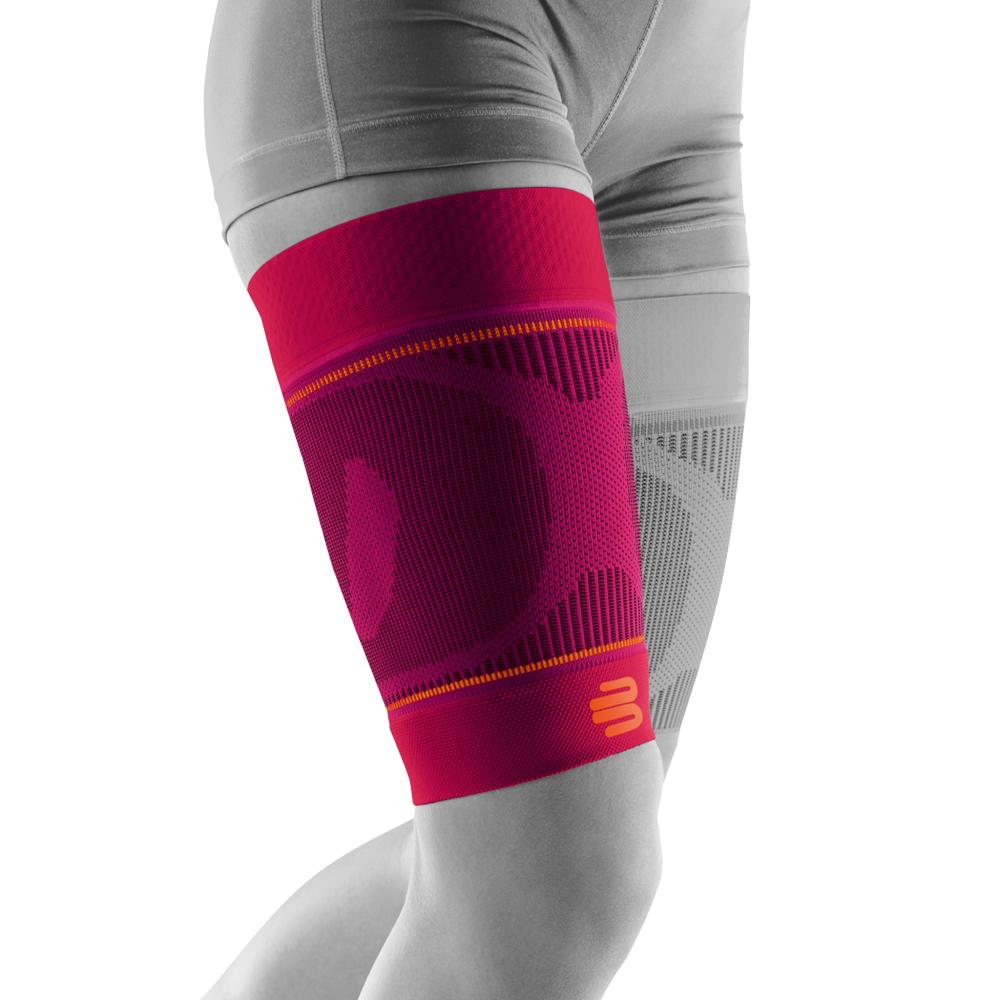
- Use of supports, e.g. sports compression for the thigh
Bauerfeind Sports Compression Lower Leg – effective support
Bauerfeind Sports Compression Lower Leg Compression Sleeve:
- Provides graduated compression that improves blood circulation and helps reduce muscle fatigue .
- Stabilizes the lower leg muscles, which indirectly relieves the upper thigh, especially during intense exercise.
- Reduces muscle vibrations and the risk of microtrauma or cramps.
- It is recommended to wear during and after sports to promote faster recovery .
*This article is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.