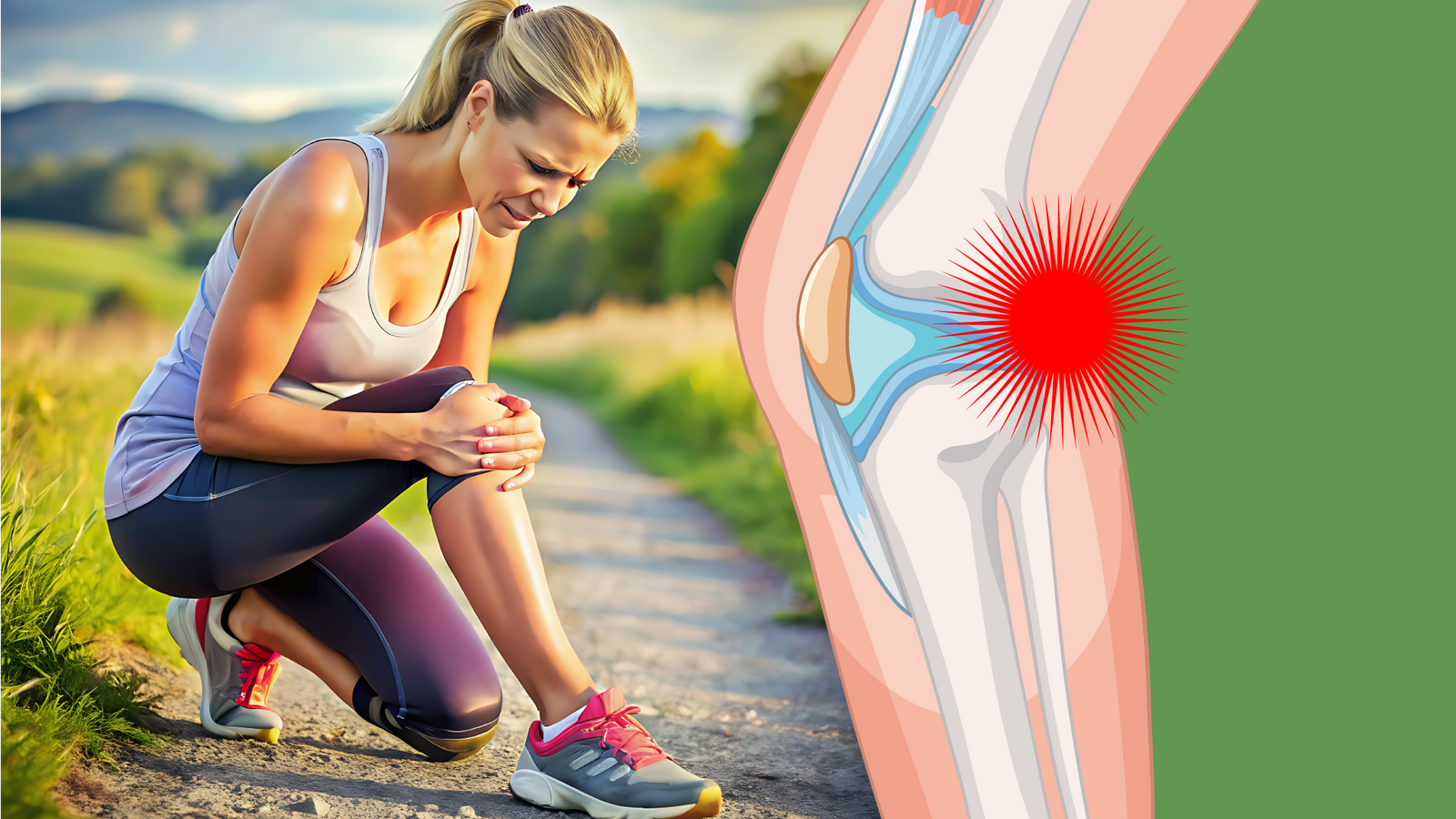
Pain in the back of the knee can have a variety of causes. It can be temporary and related to overuse or injury, but it can also be a sign of more serious health problems.
Possible causes of pain in the back of the knee joint:

- Muscle or tendon injuries : Overuse or too much tension can cause inflammation or injury to the muscles or tendons, especially in the hamstring region.
- Knee cyst (Baker cyst) : Fluid buildup in the knee joint can form a cyst at the back of the knee, causing pain and swelling.
- Meniscus damage : A tear or damage to the meniscus can cause pain, including in the back of the knee, especially if there is movement restriction.
- Nerve compression : Several nerves run along the back of the knee, and their irritation or compression, such as from a cyst or injury, can cause pain.
- Vascular problems : Varicose veins or blood vessel damage, such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT), can cause pain and swelling in this area.
If you are experiencing pain in the back of your knee, it is recommended that you consult a doctor or physiotherapist to determine the exact cause of the pain and receive appropriate treatment.
https://vc4.lv/pakalpojumi/arstnieciba/traumatologija-ortopedija/
Treatment methods can vary and depend on the cause of the pain:
- Rest : Avoid activities that cause discomfort or increase pain to reduce stress on the knee joint.
- Ice packs : Apply an ice pack to the painful area for 15-20 minutes several times a day to reduce inflammation and swelling.
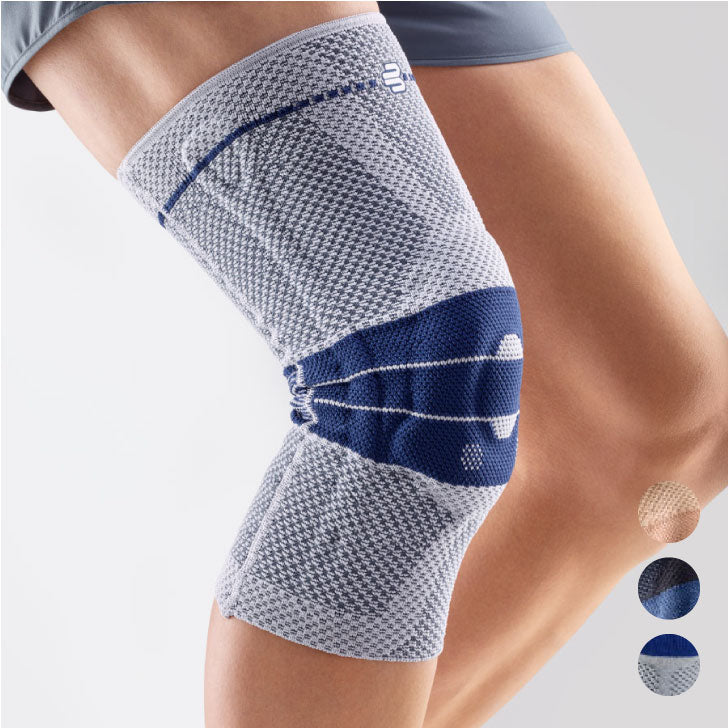
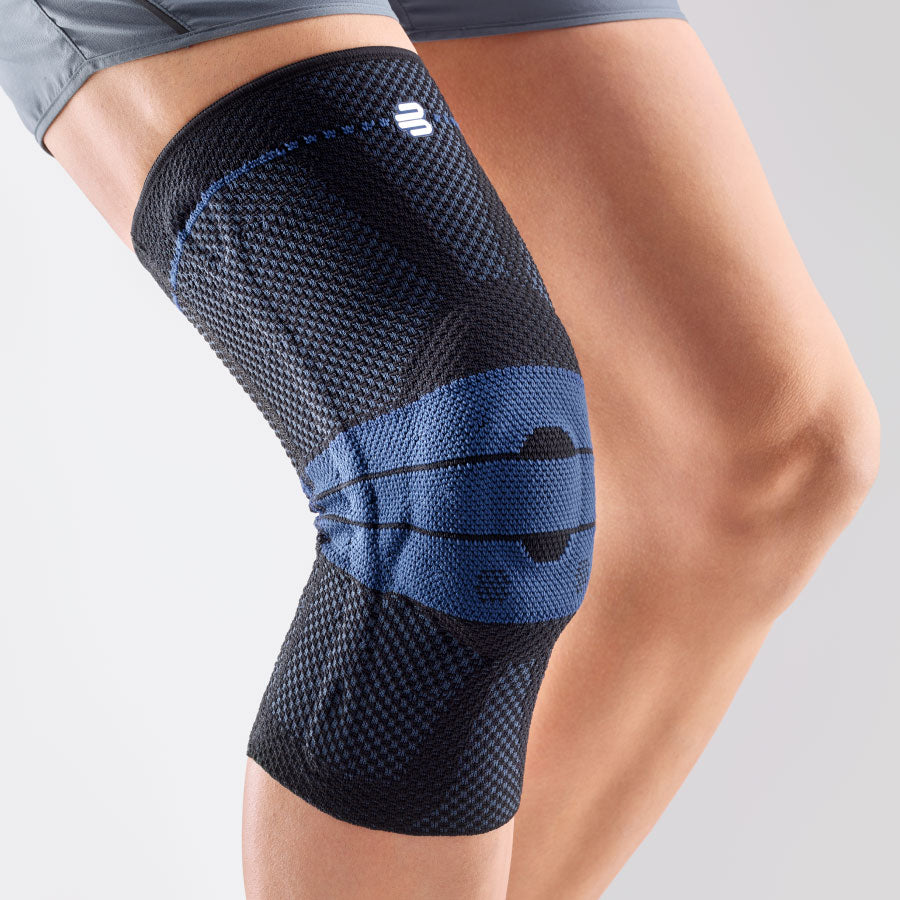
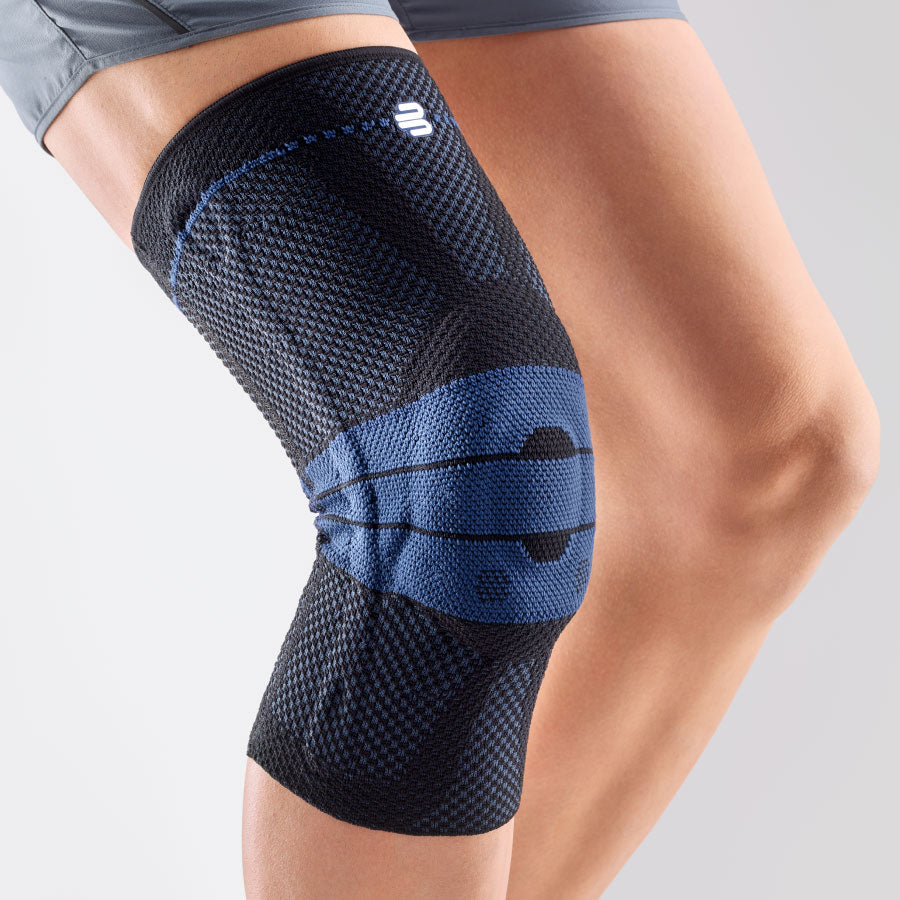
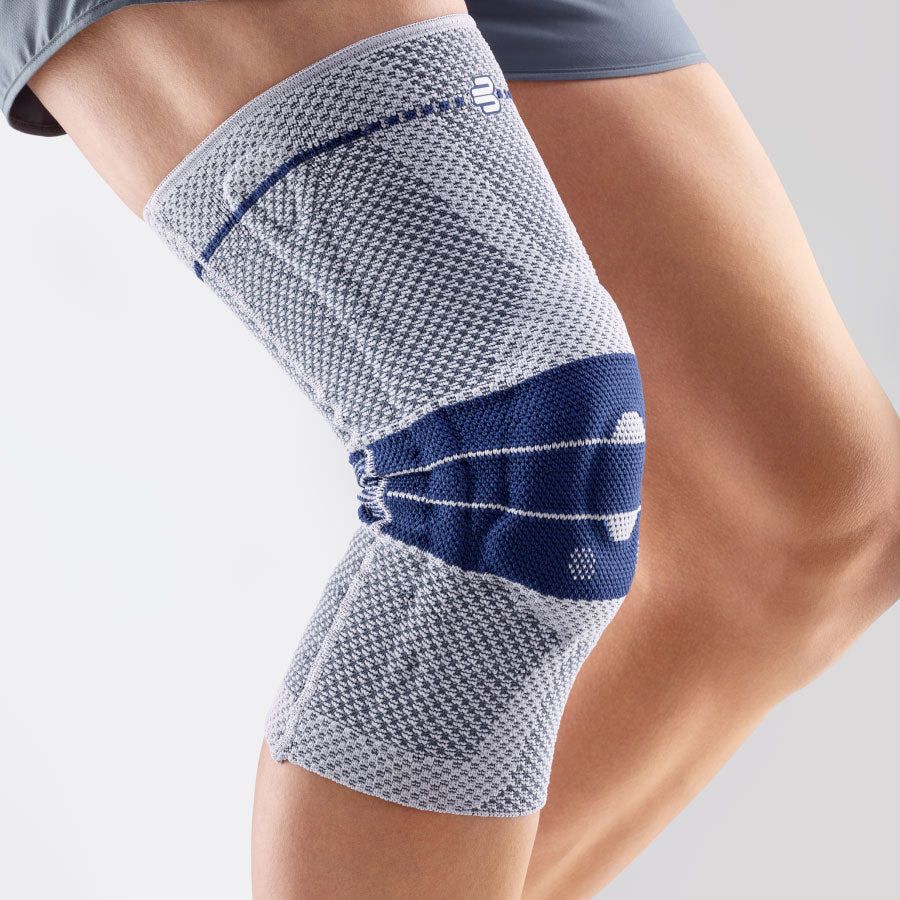
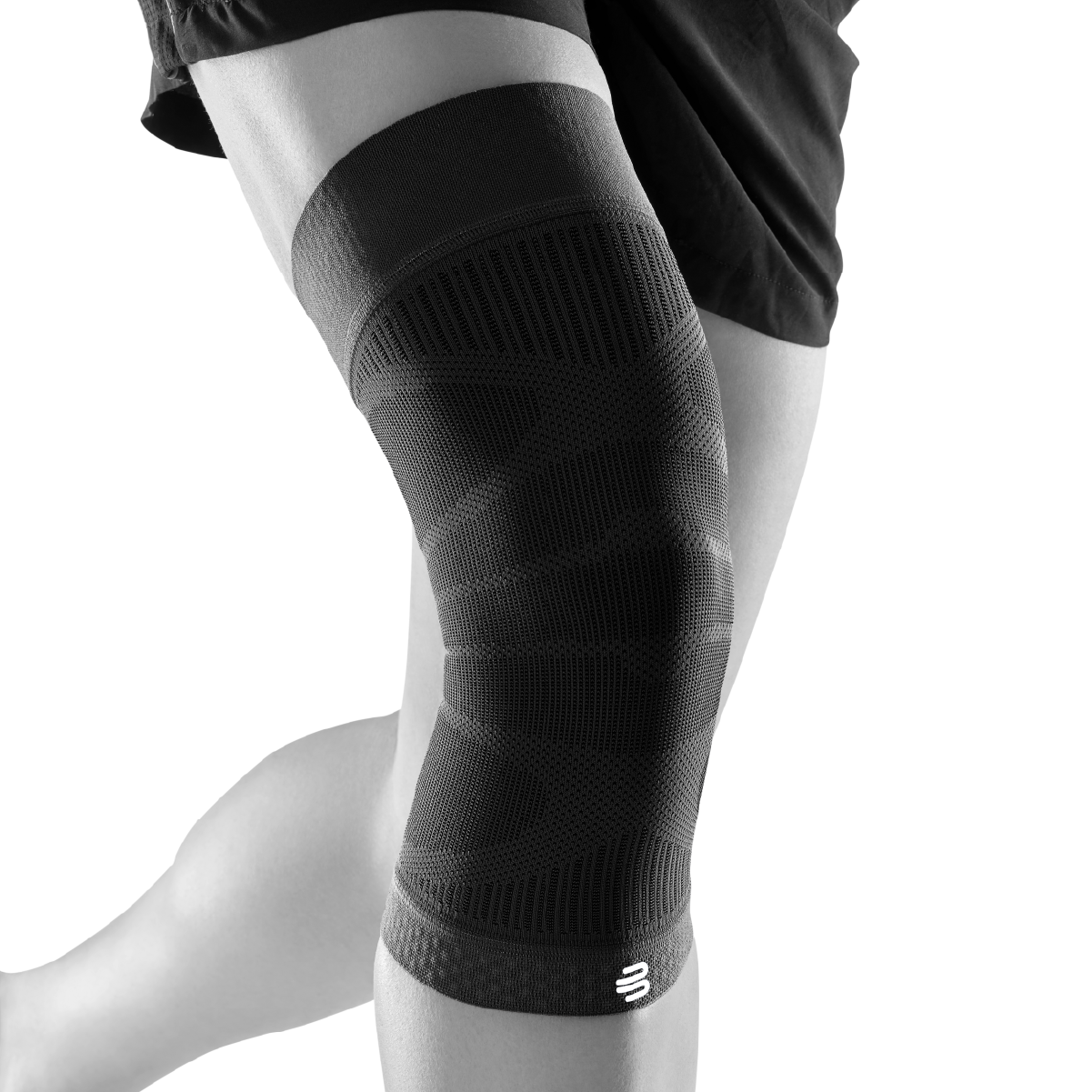
- Orthoses or elastic bandages : Orthoses or knee braces can help stabilize the joint and support the muscles, as well as reduce movement restrictions.
- Painkillers : Over-the-counter painkillers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help reduce pain and inflammation. In more severe cases, your doctor may prescribe stronger medications.
- Physical therapy : A physical therapist can develop an exercise plan to strengthen the muscles around the knee joint, improve mobility, and reduce tension in the tendons and muscles.
- Surgical intervention : If the pain is caused by, for example, a Baker's cyst, a meniscus tear, or another structural problem, your doctor may recommend a surgical solution to repair the damage.
- Treatment for vascular problems : If the pain is related to vein or blood vessel problems, such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT), your doctor may recommend medication, compression stockings, or other techniques to improve blood circulation.
It is important to remember that self-medication can worsen your condition. If you experience severe pain or pain that does not subside, be sure to seek medical attention.
Check out Bauerfeind orthoses and sports compression: https://dynasty.lv/collections/ortozes-bandazas-atbalsti-celim-un-guzai