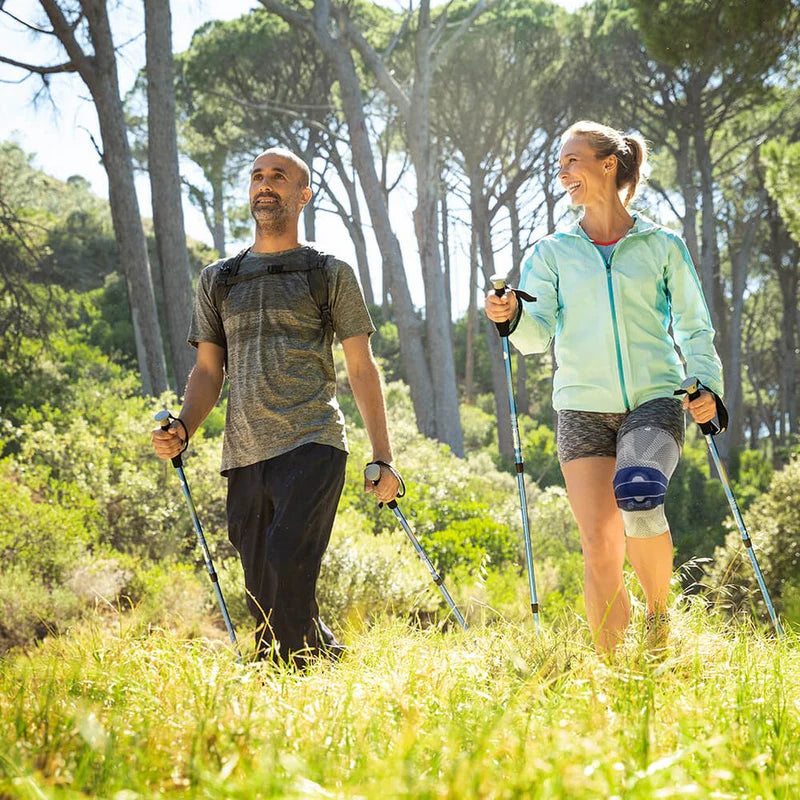
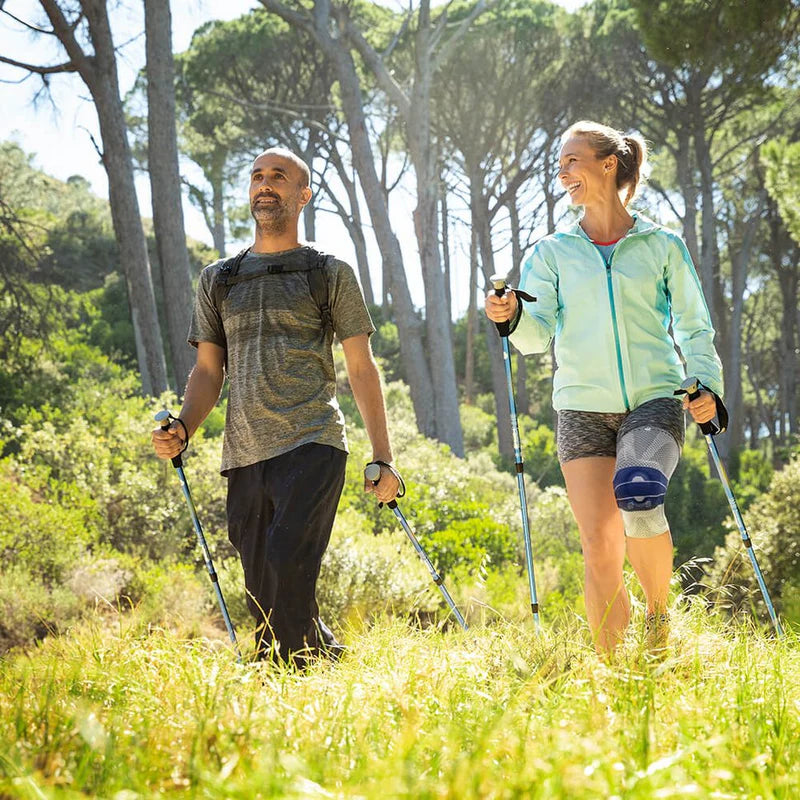
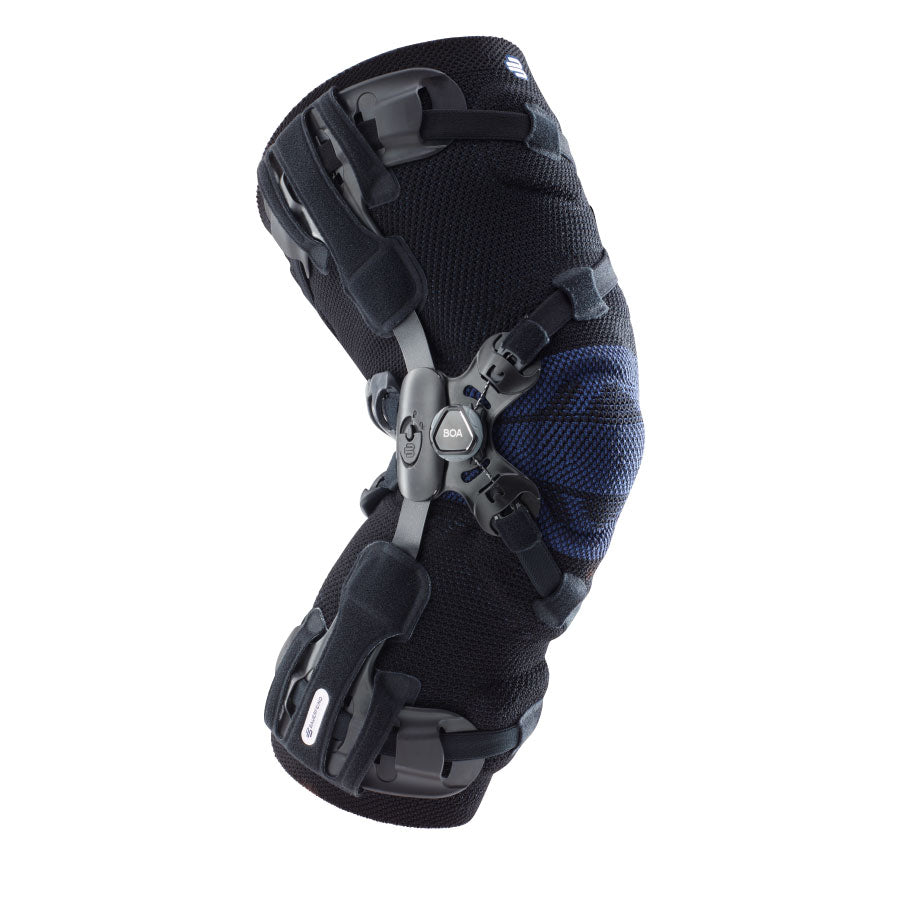
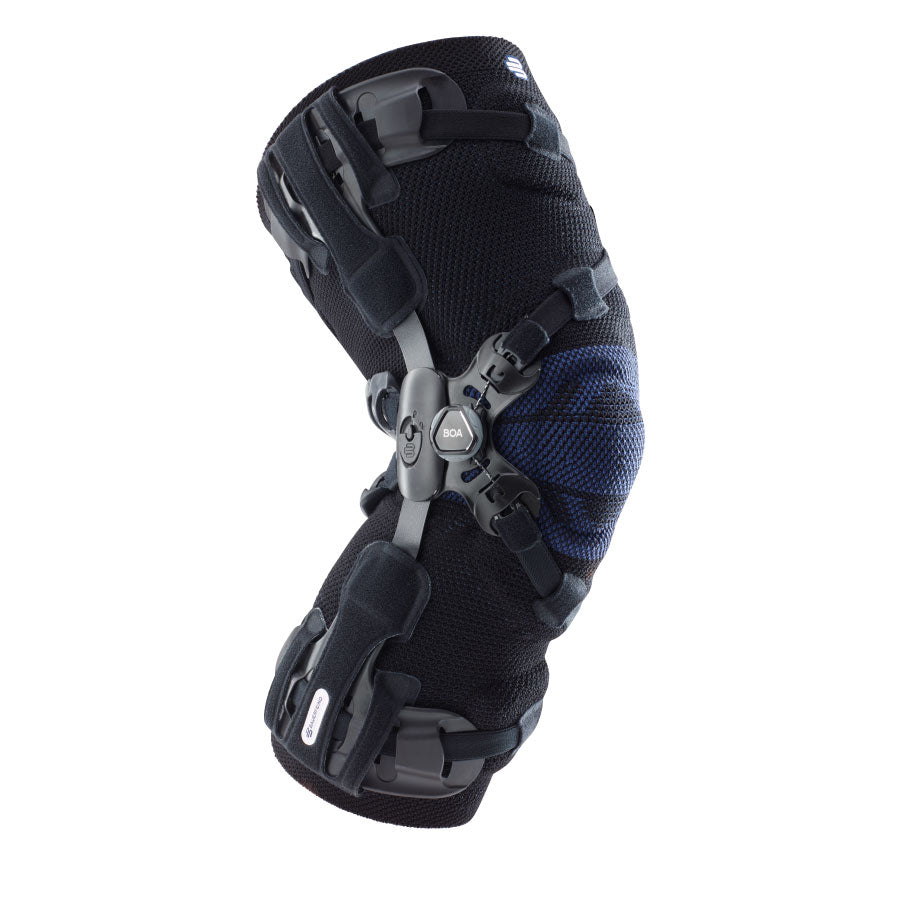
Gonarthrosis is a type of arthritis that affects the knee joint. It causes pain, stiffness, and joint damage.
Causes
- Wear and tear and aging: Age-related changes in cartilage and bone structure can lead to gonarthrosis.
- Trauma: Knee injuries, such as fractures or sprains, can increase the risk of developing gonarthrosis.
- Arthritis: Rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis are other types of arthritis that can affect the knee joint.
- Obesity: Excess weight puts extra strain on the knee joints.
- Genetic predisposition: Some people have a genetic predisposition to developing gonarthrosis.
Solutions
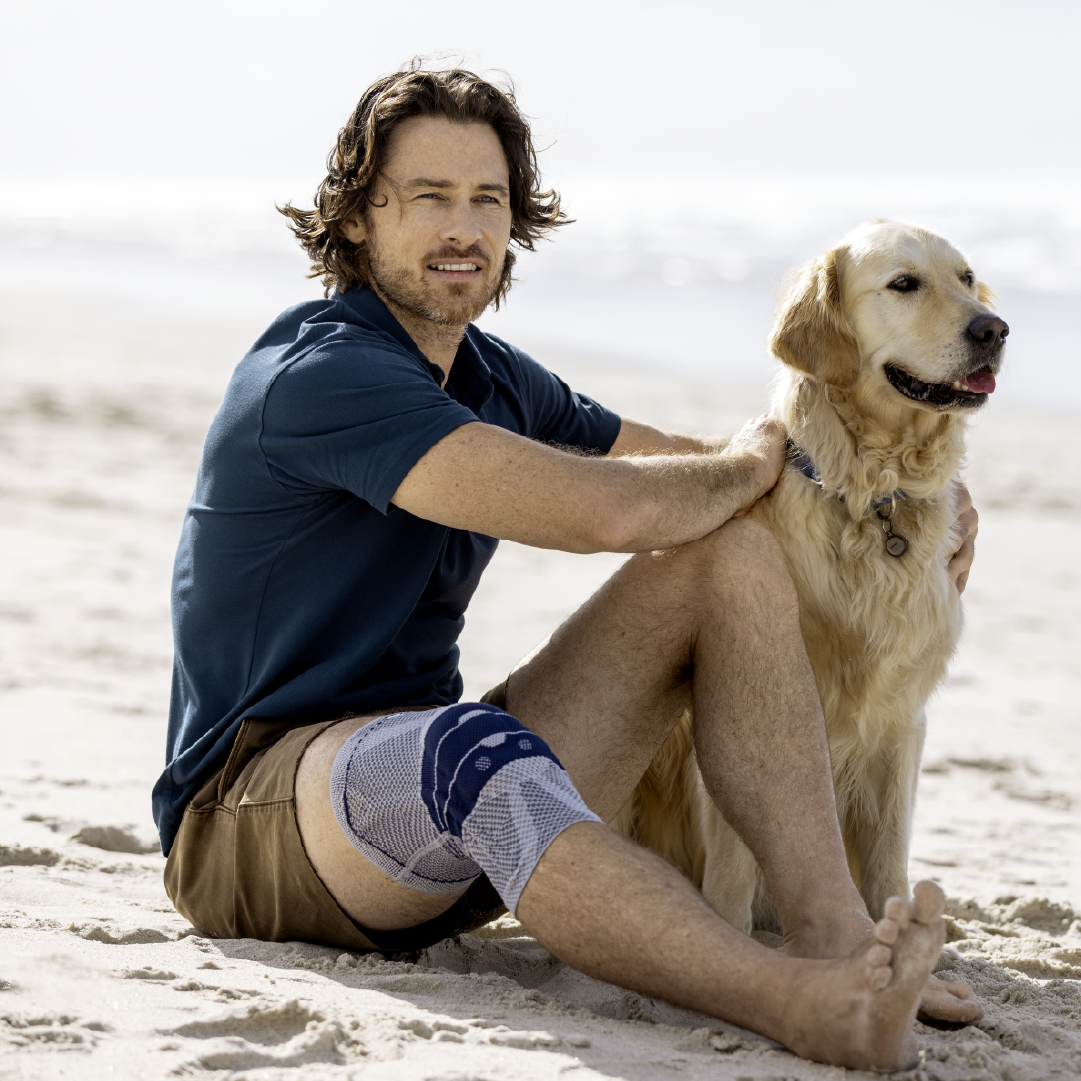
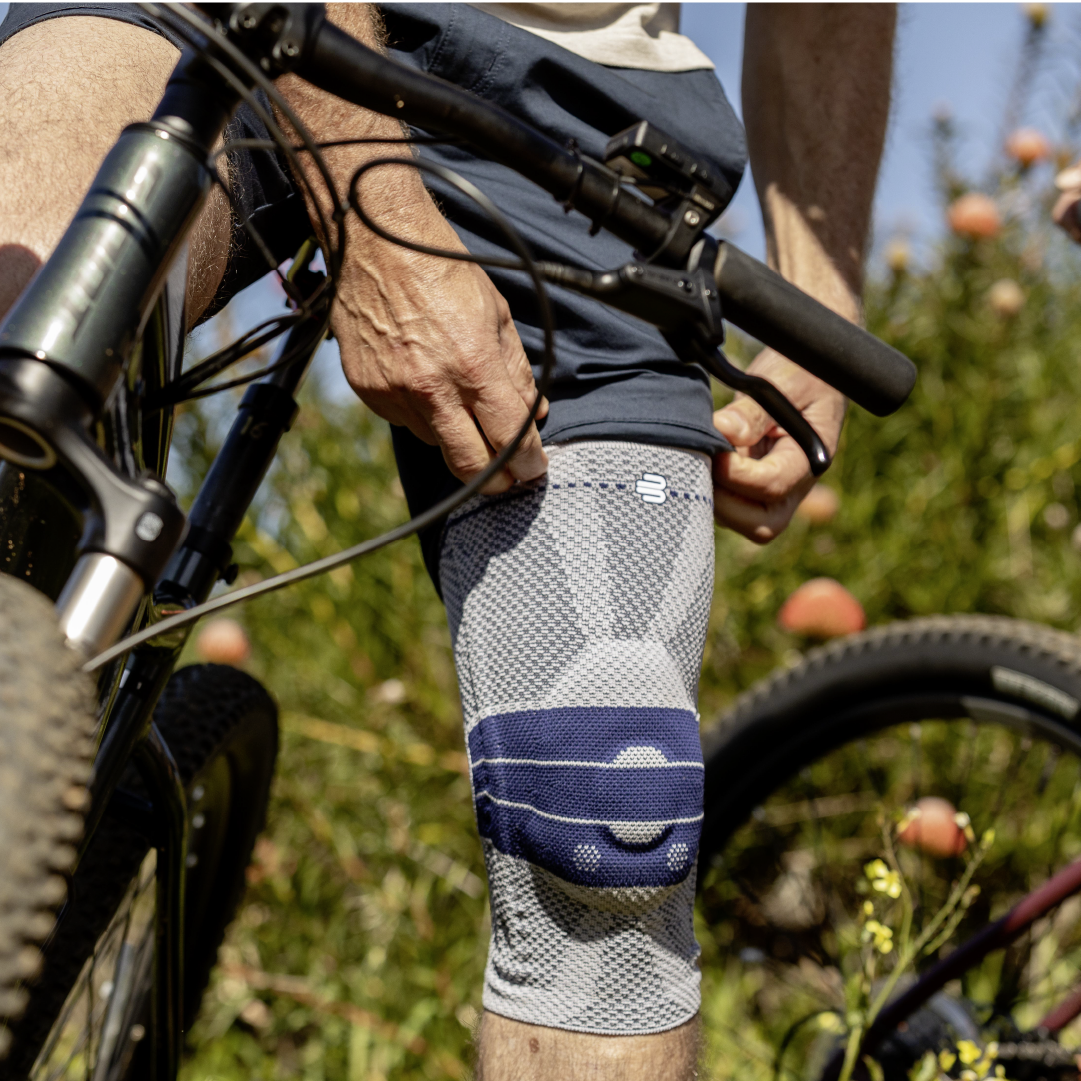
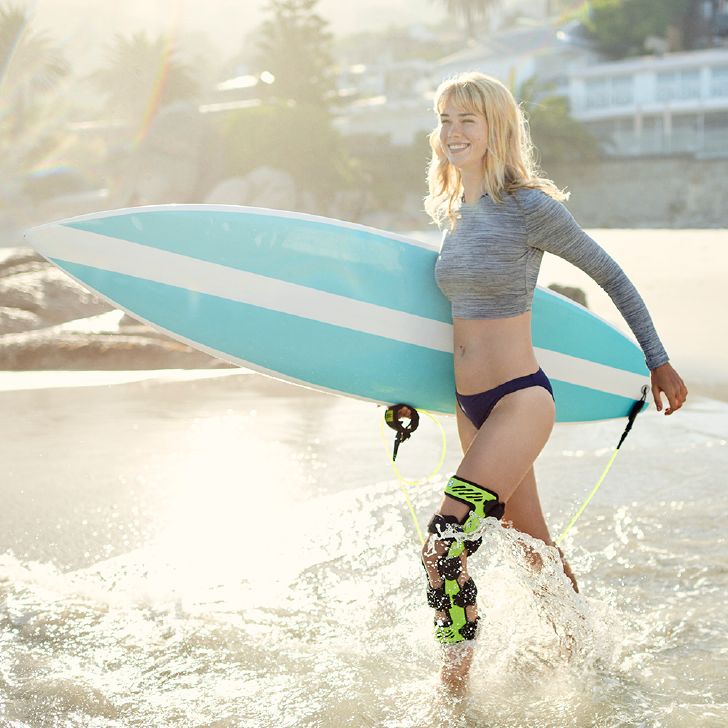
- Physical activity: Moderate physical activity, such as swimming, cycling, or water aerobics, can help strengthen the muscles around the knee joint and reduce pain.
- Weight control: If you are obese, losing weight can help reduce the strain on your knee joints.
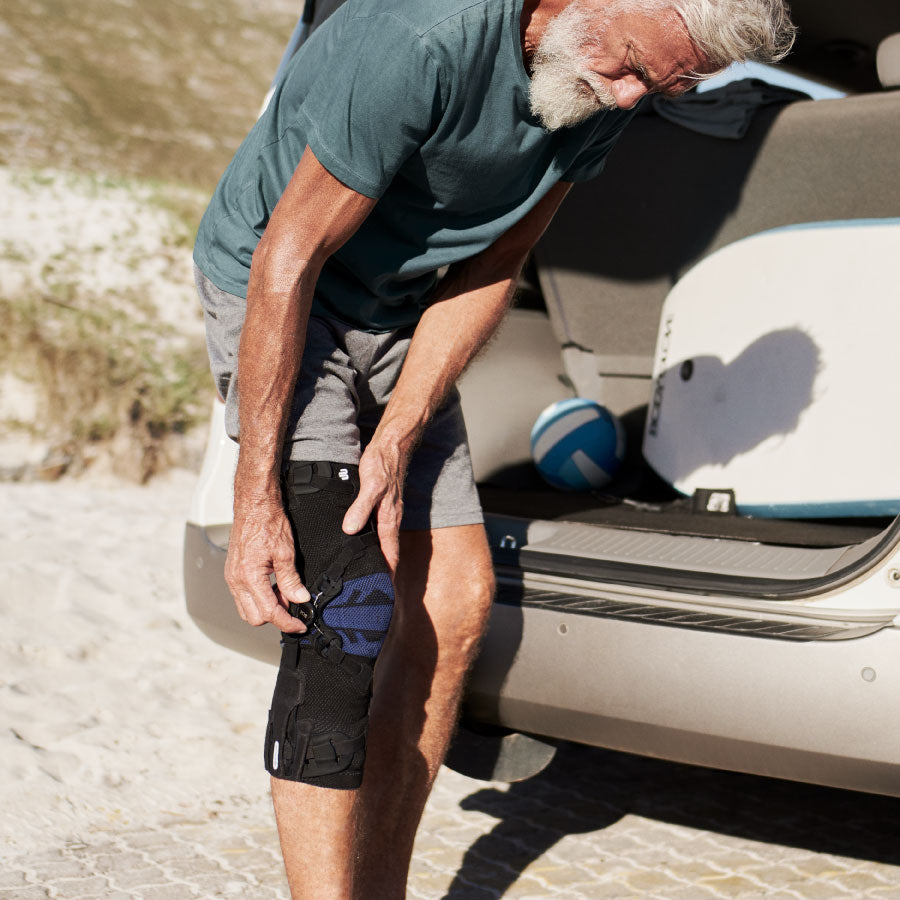
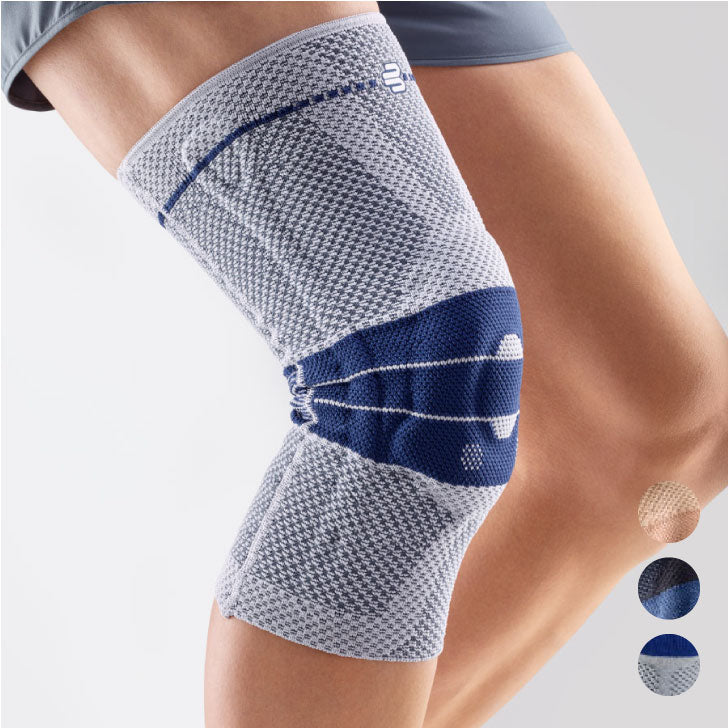
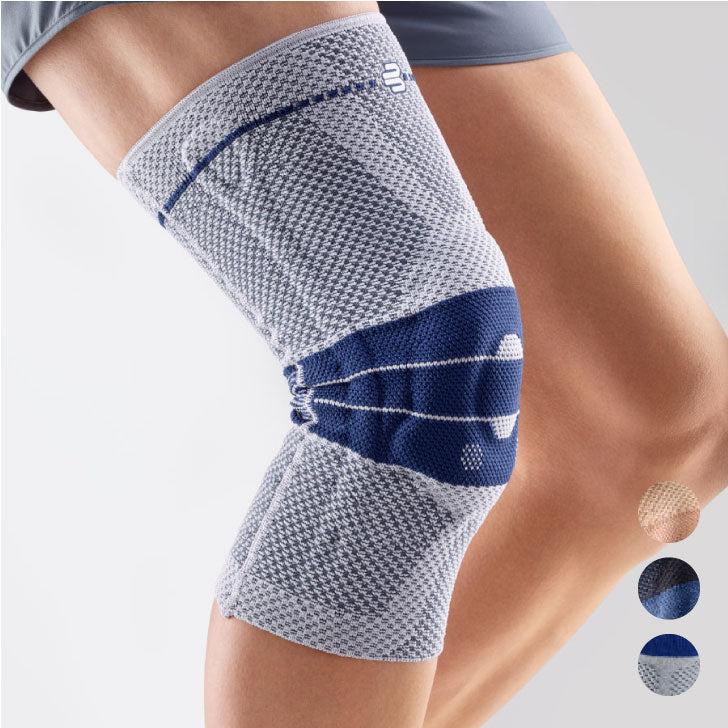
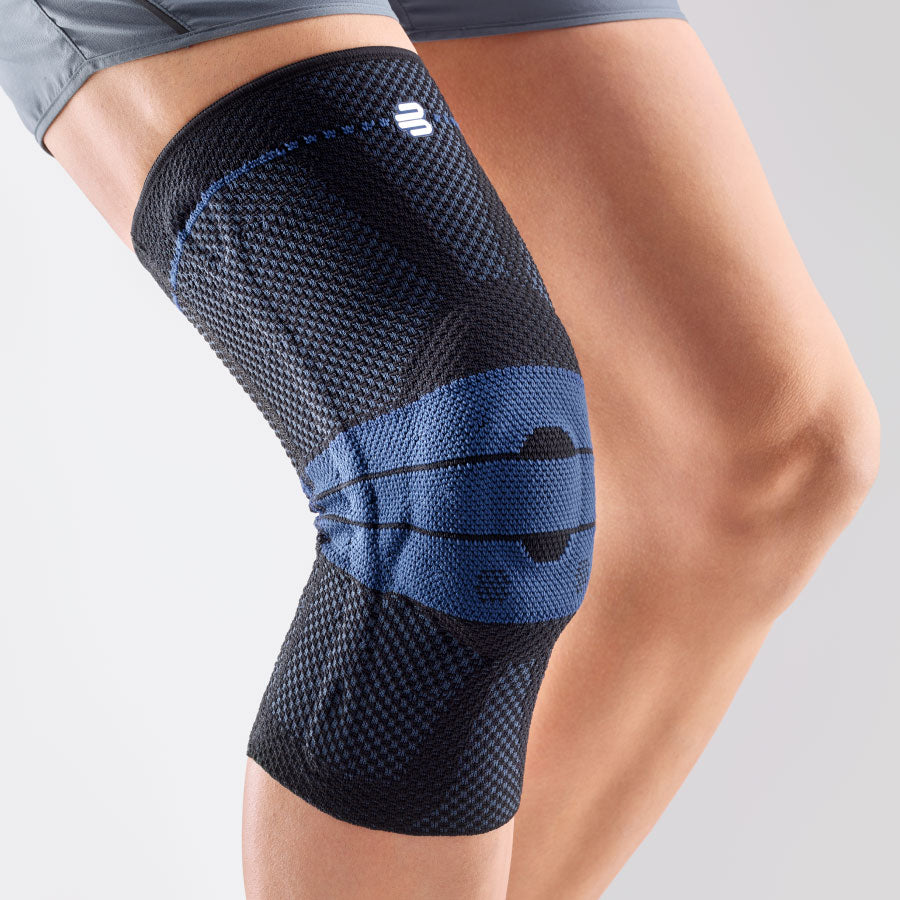
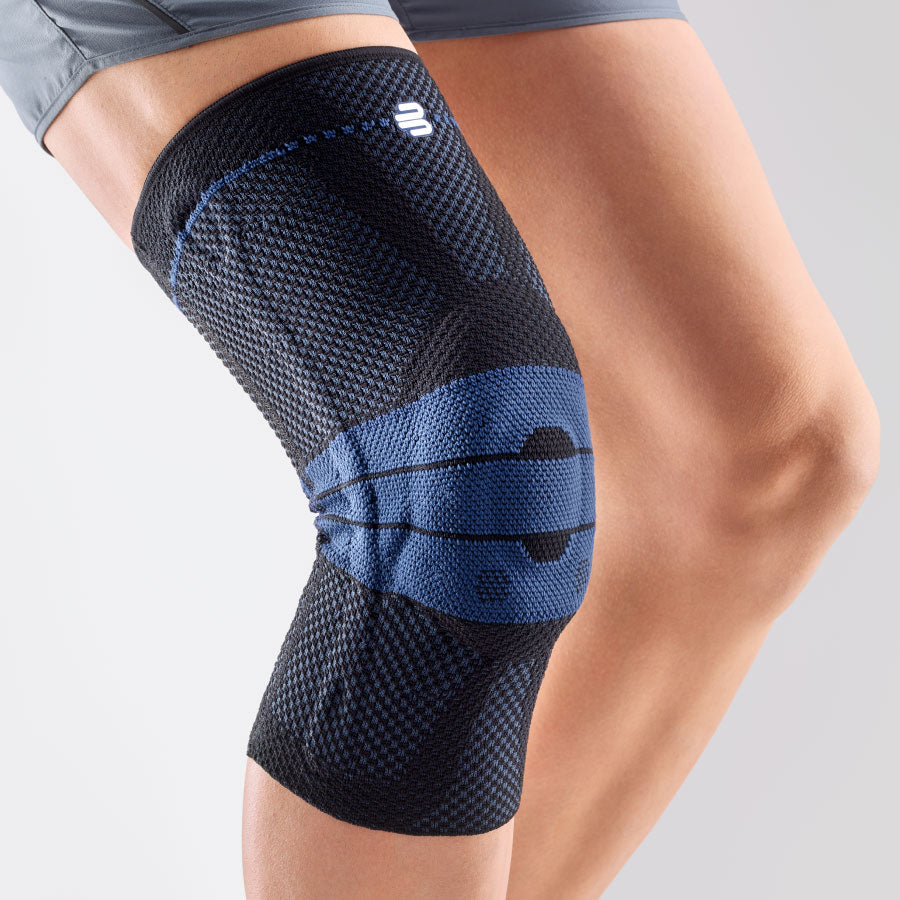
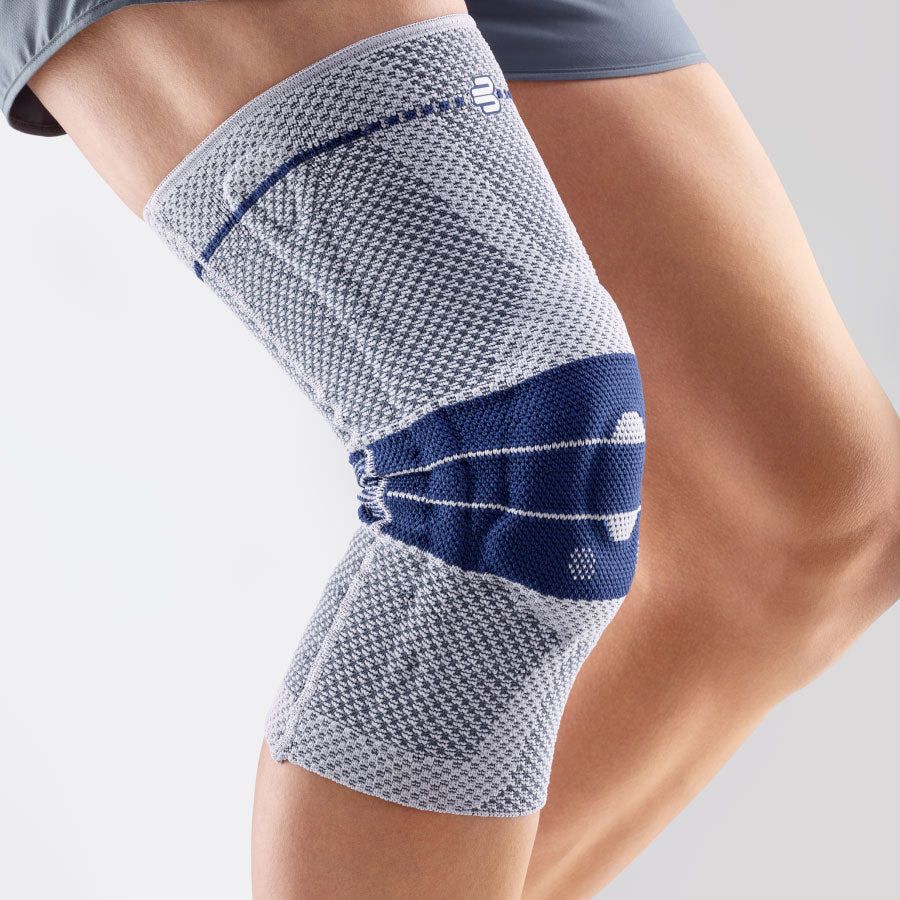
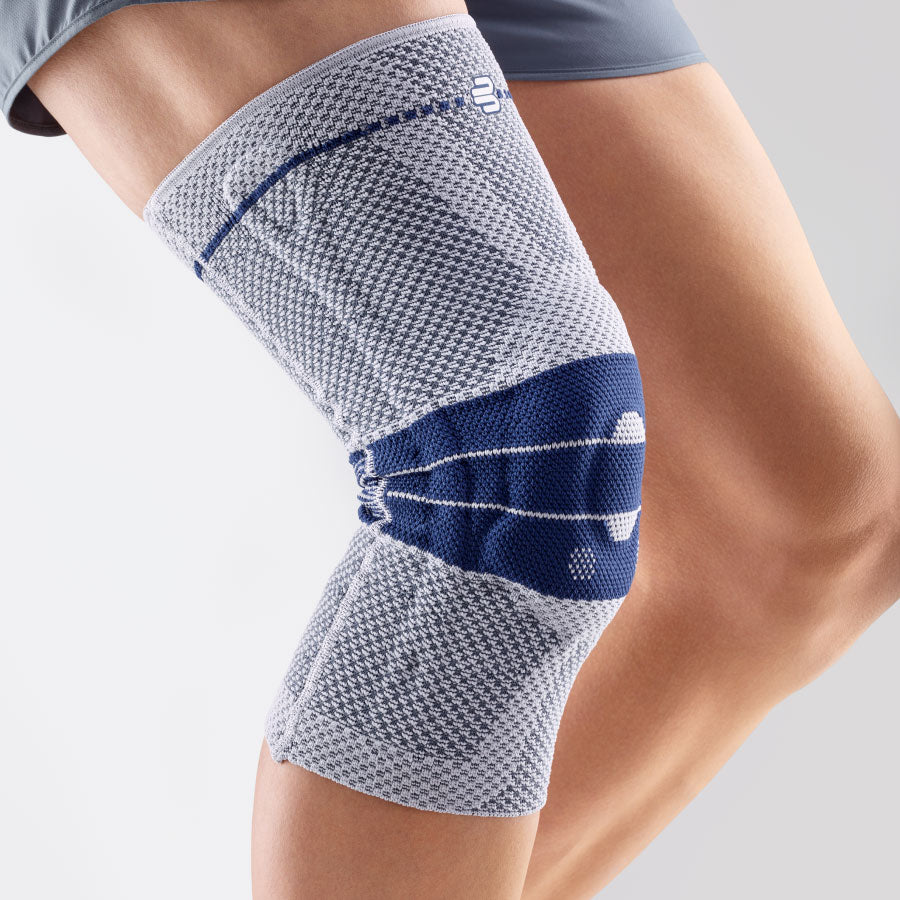
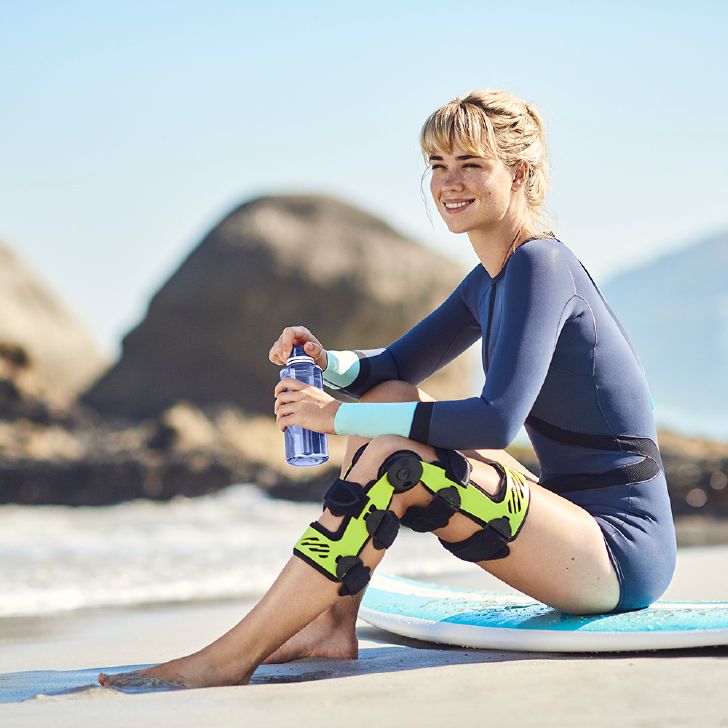
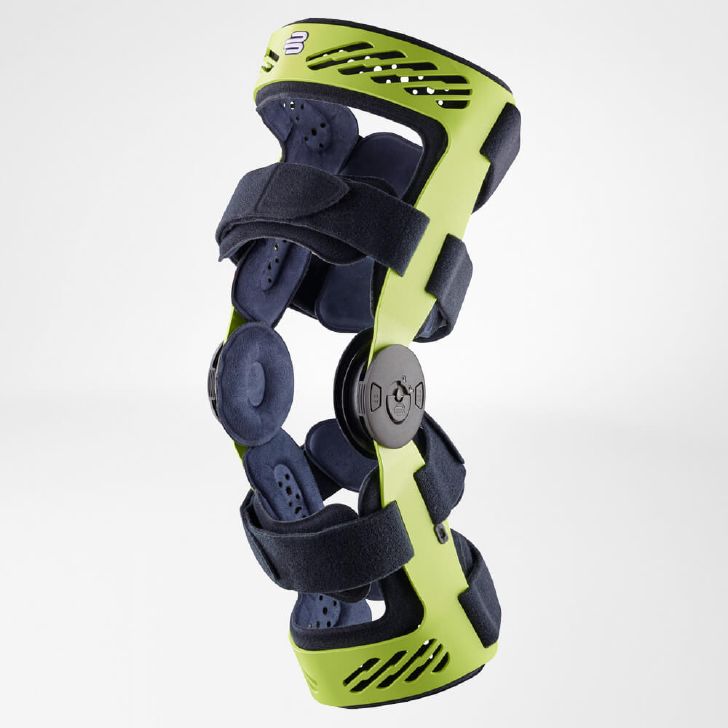
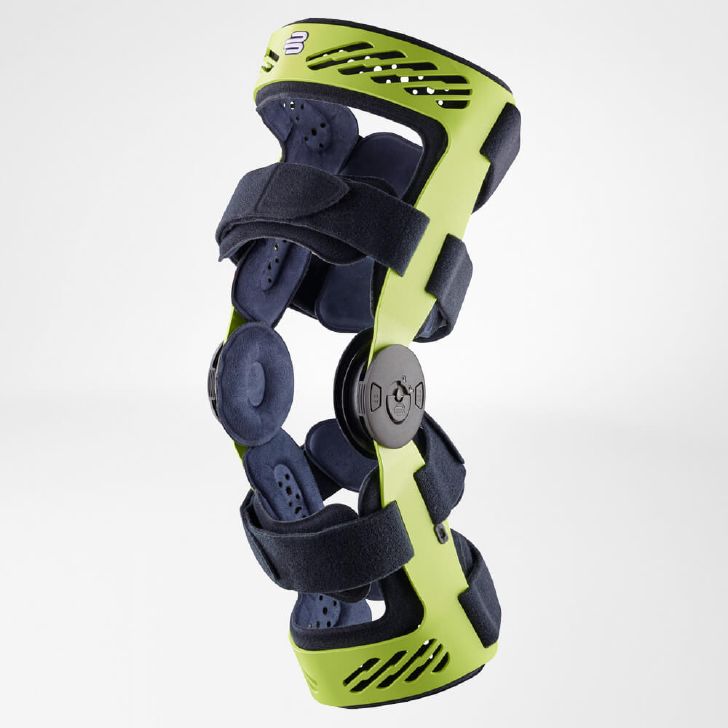
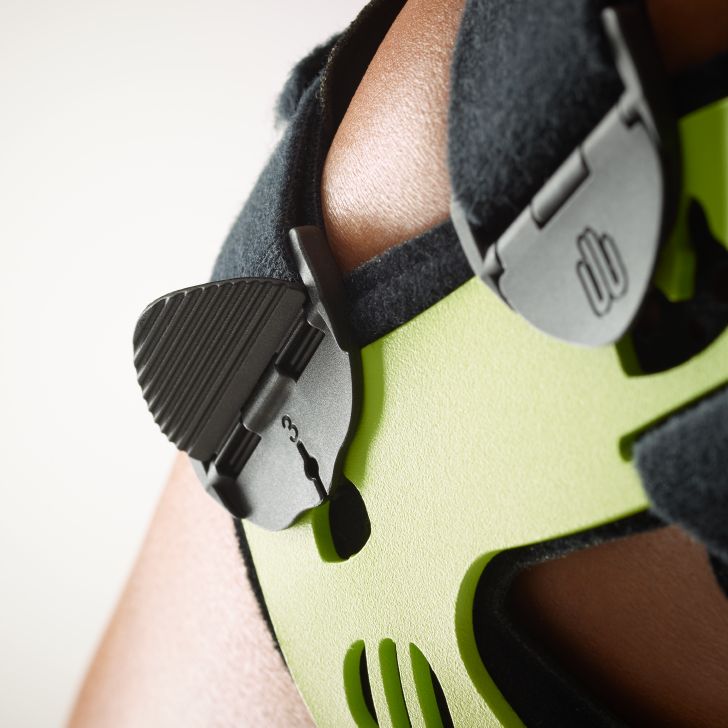
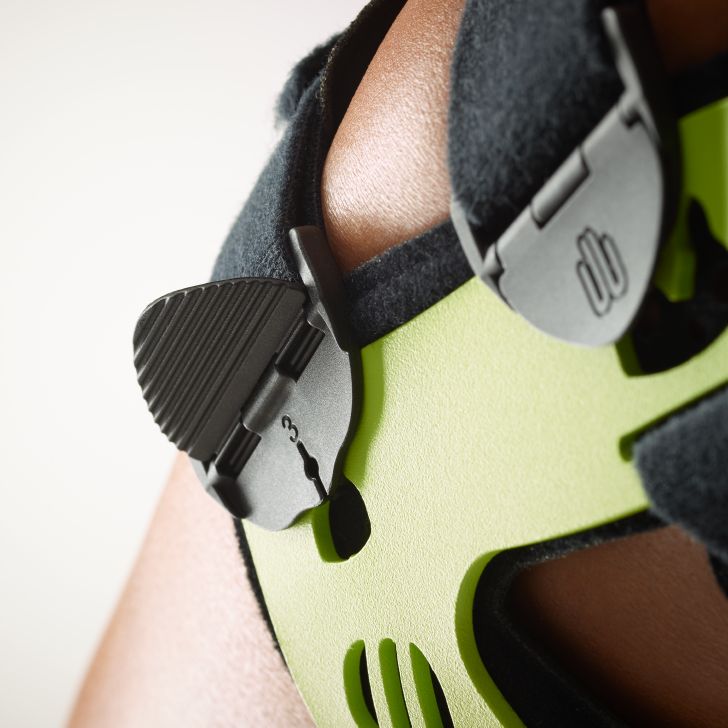
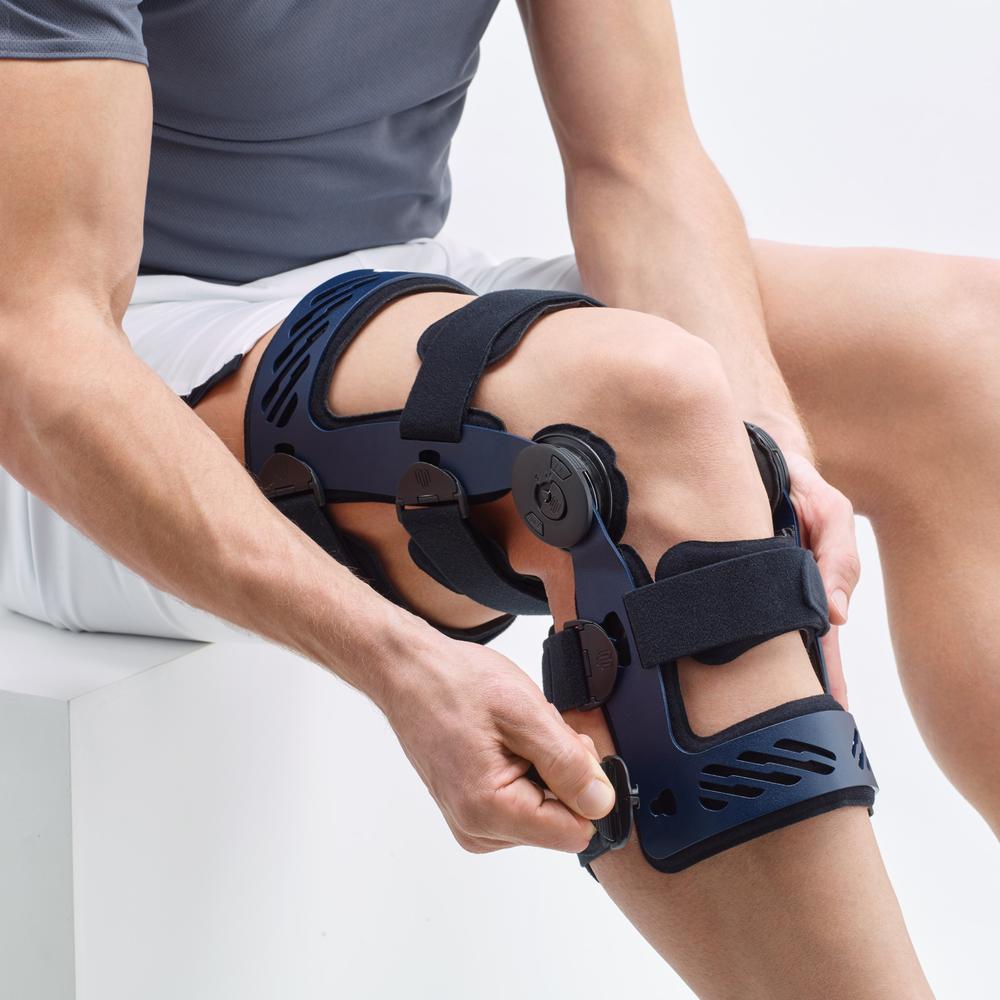
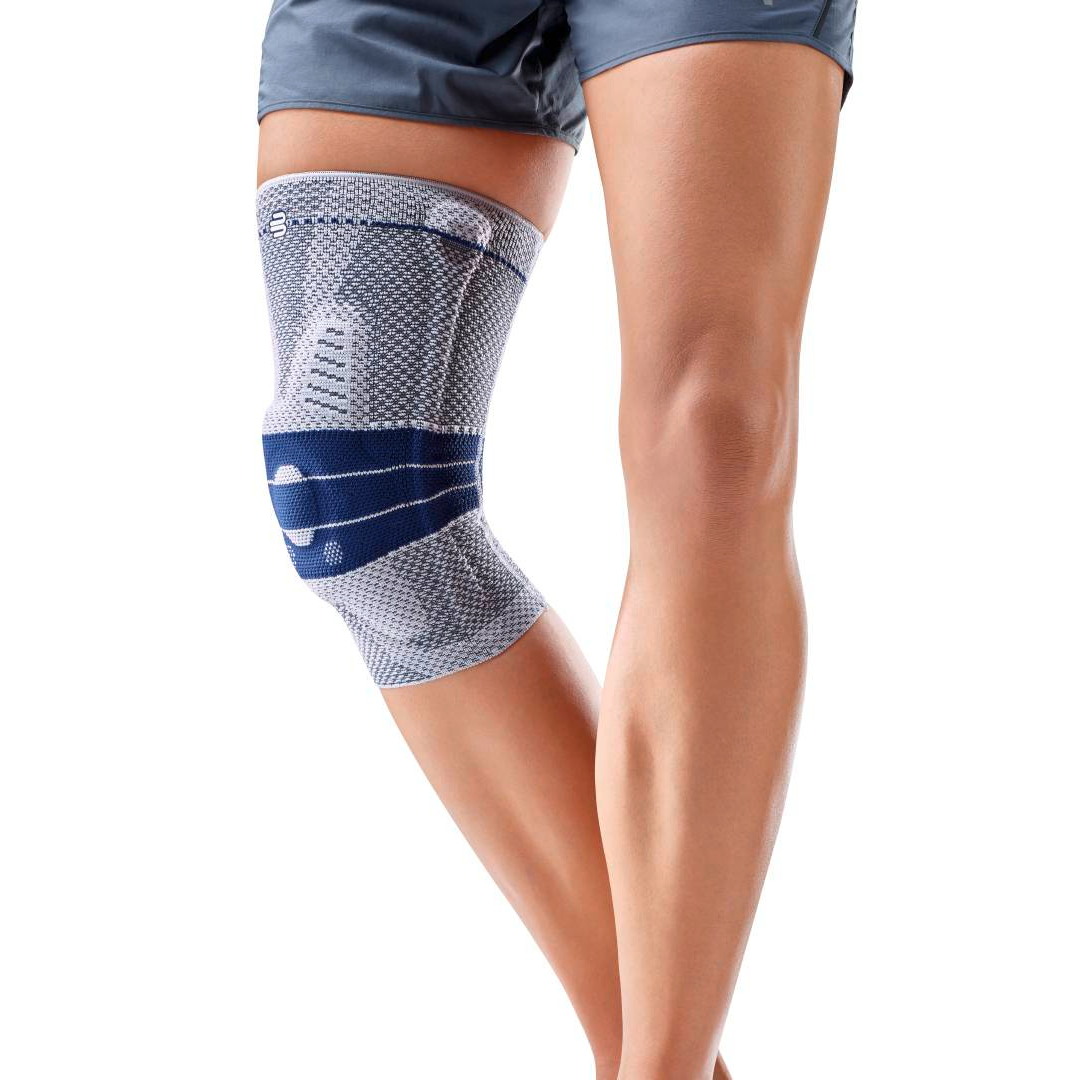
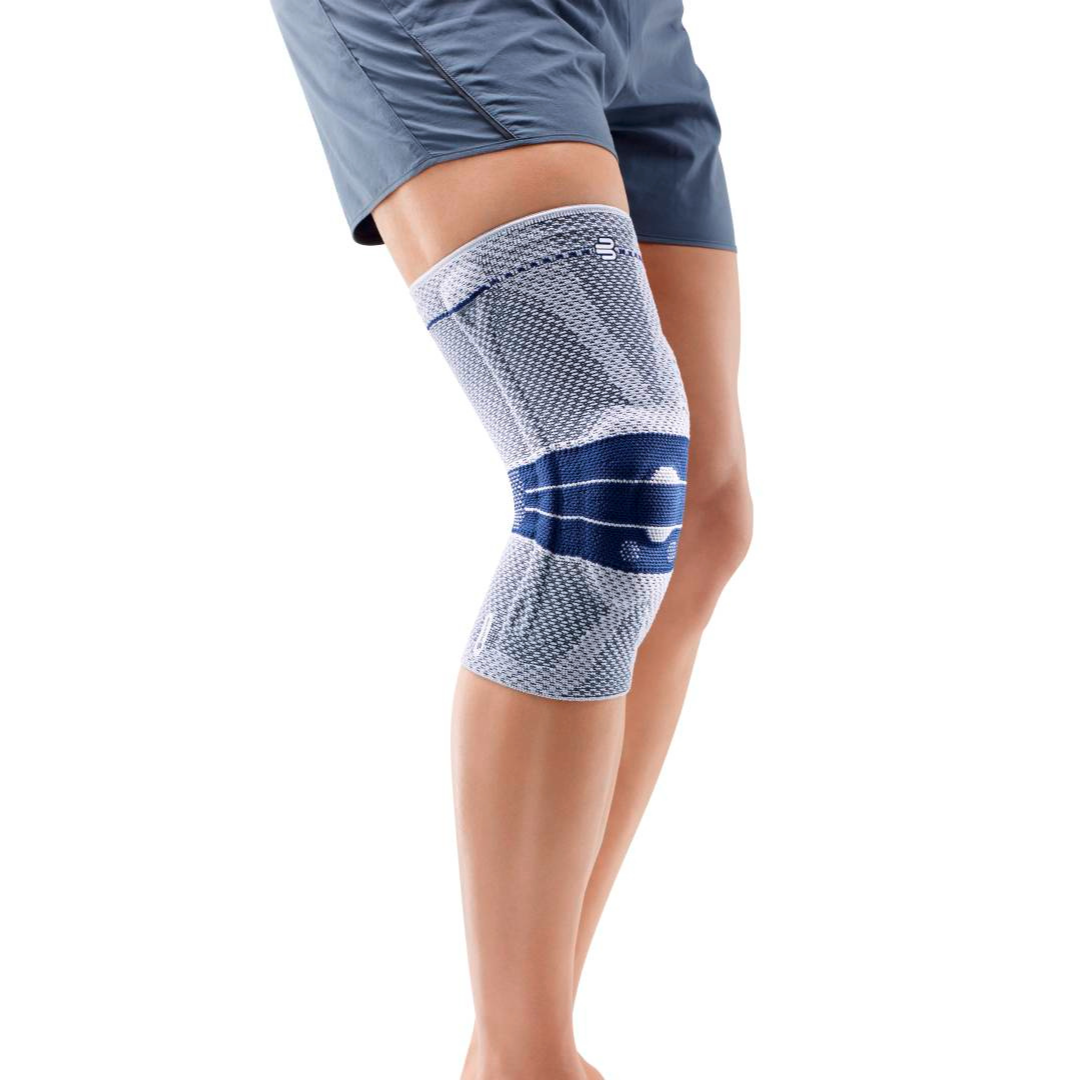
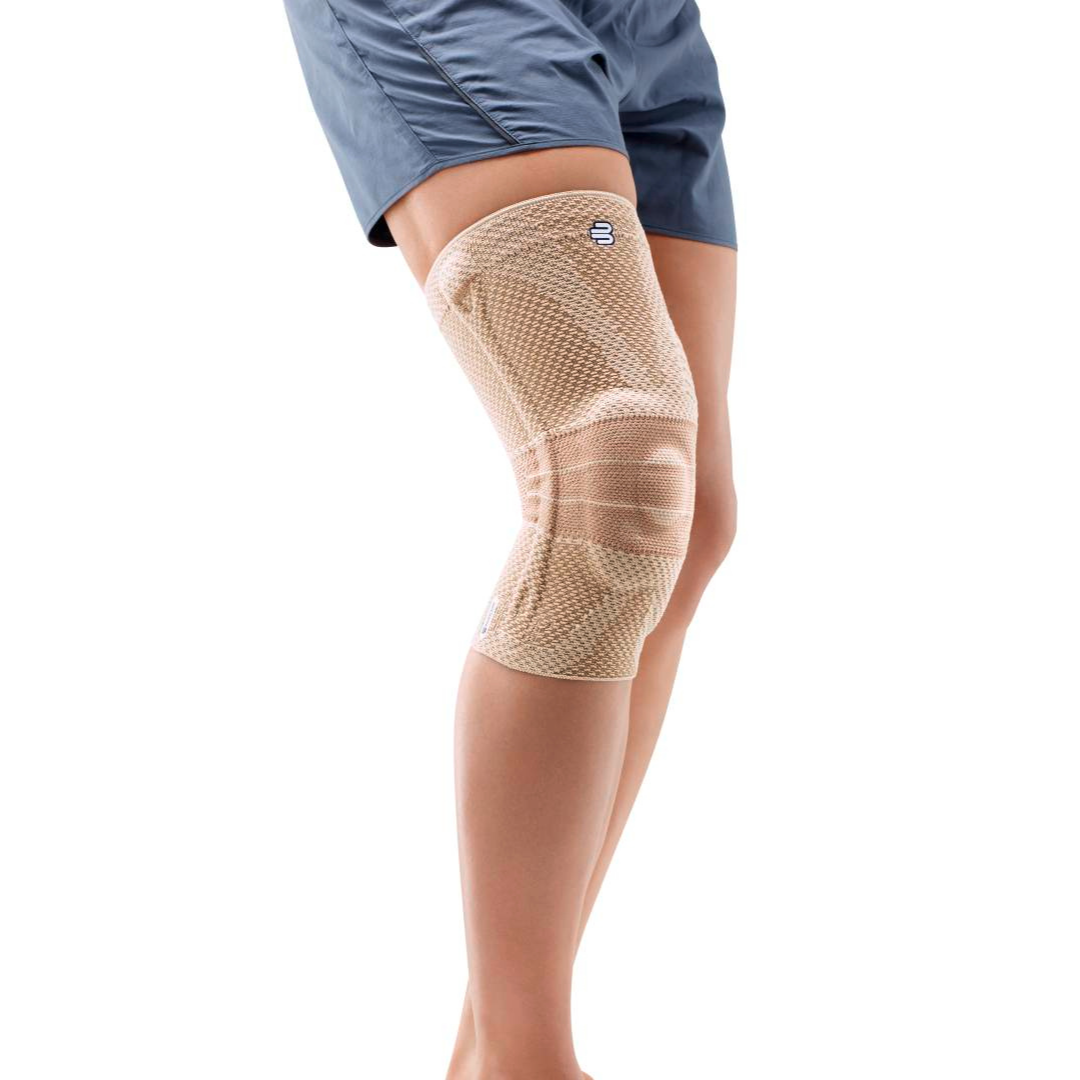
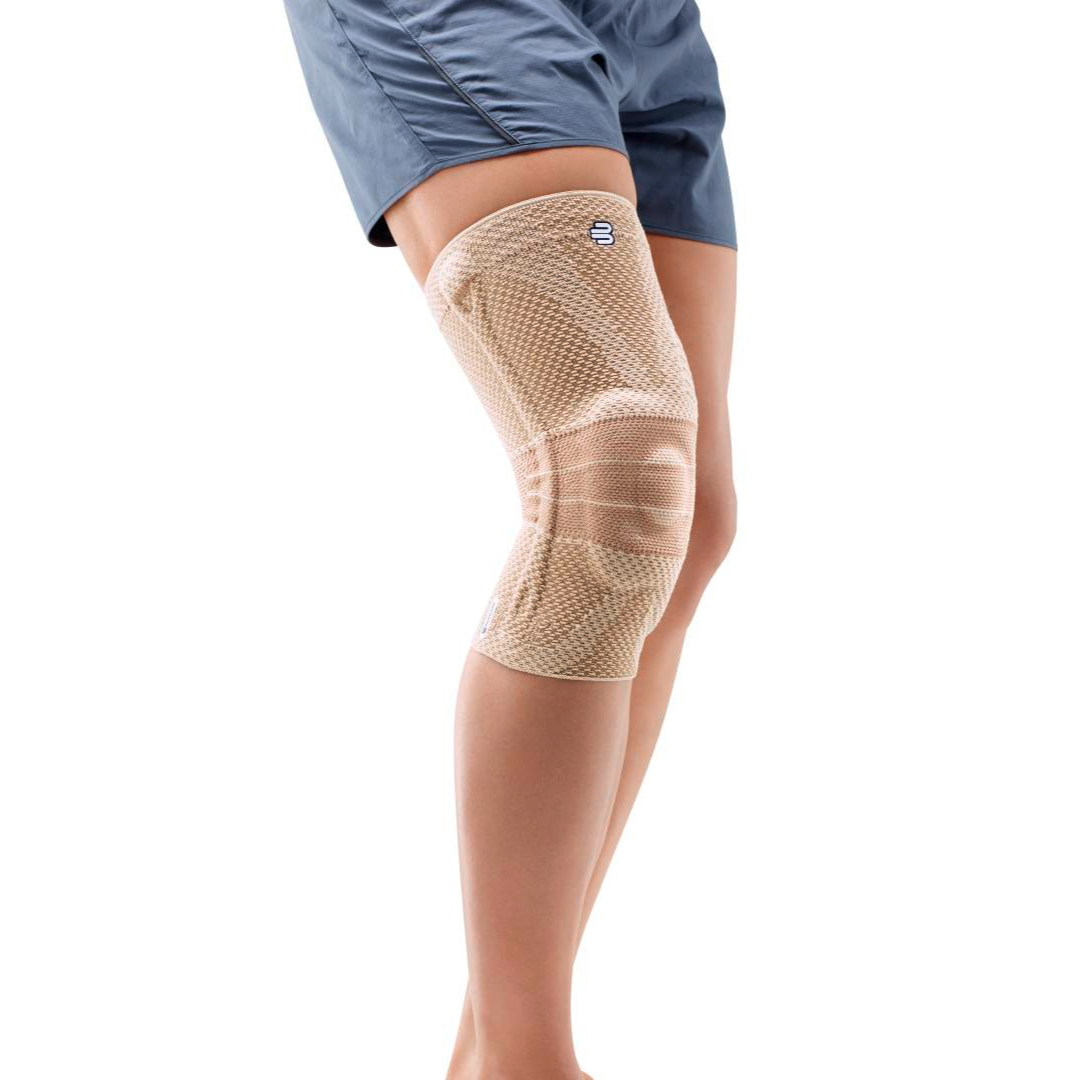
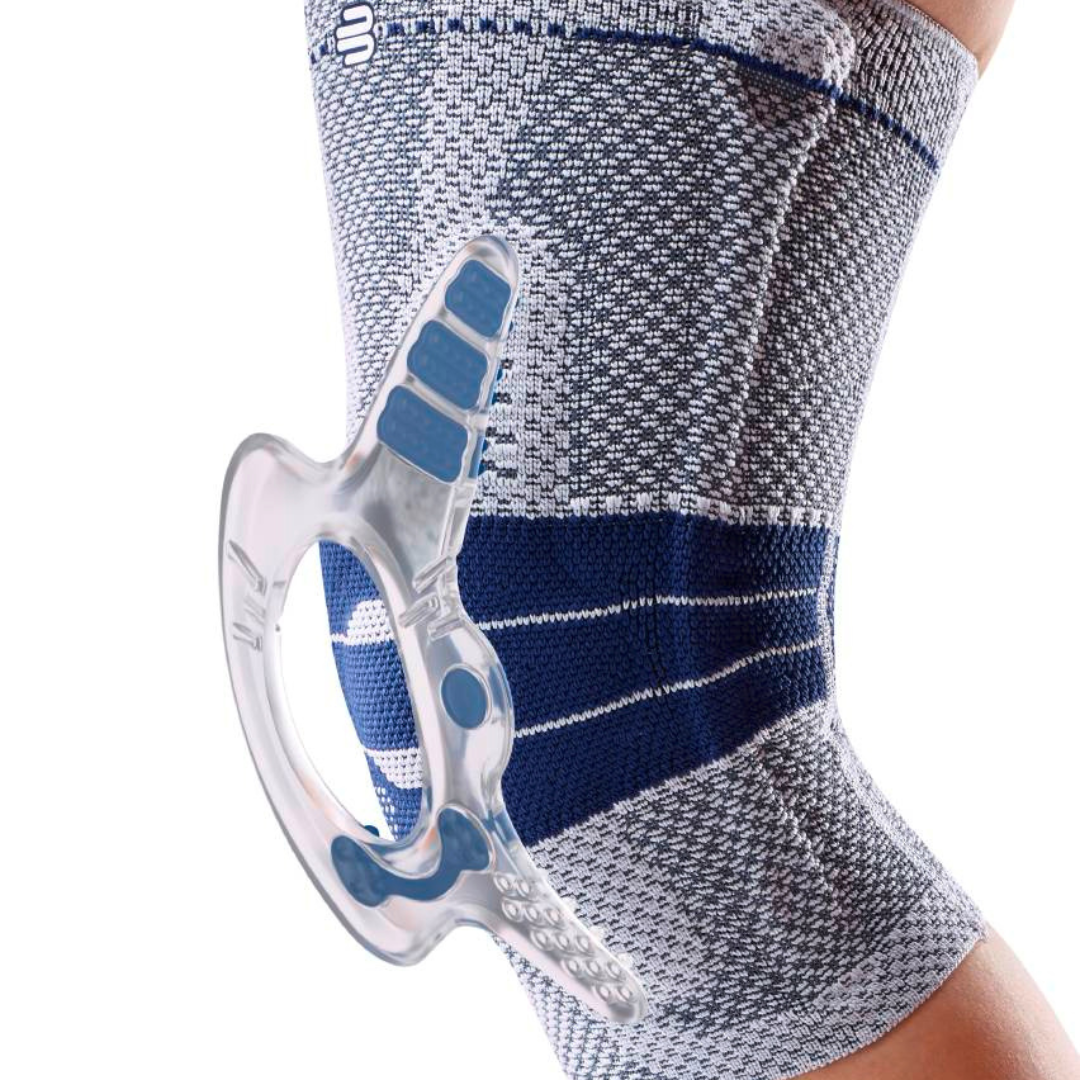
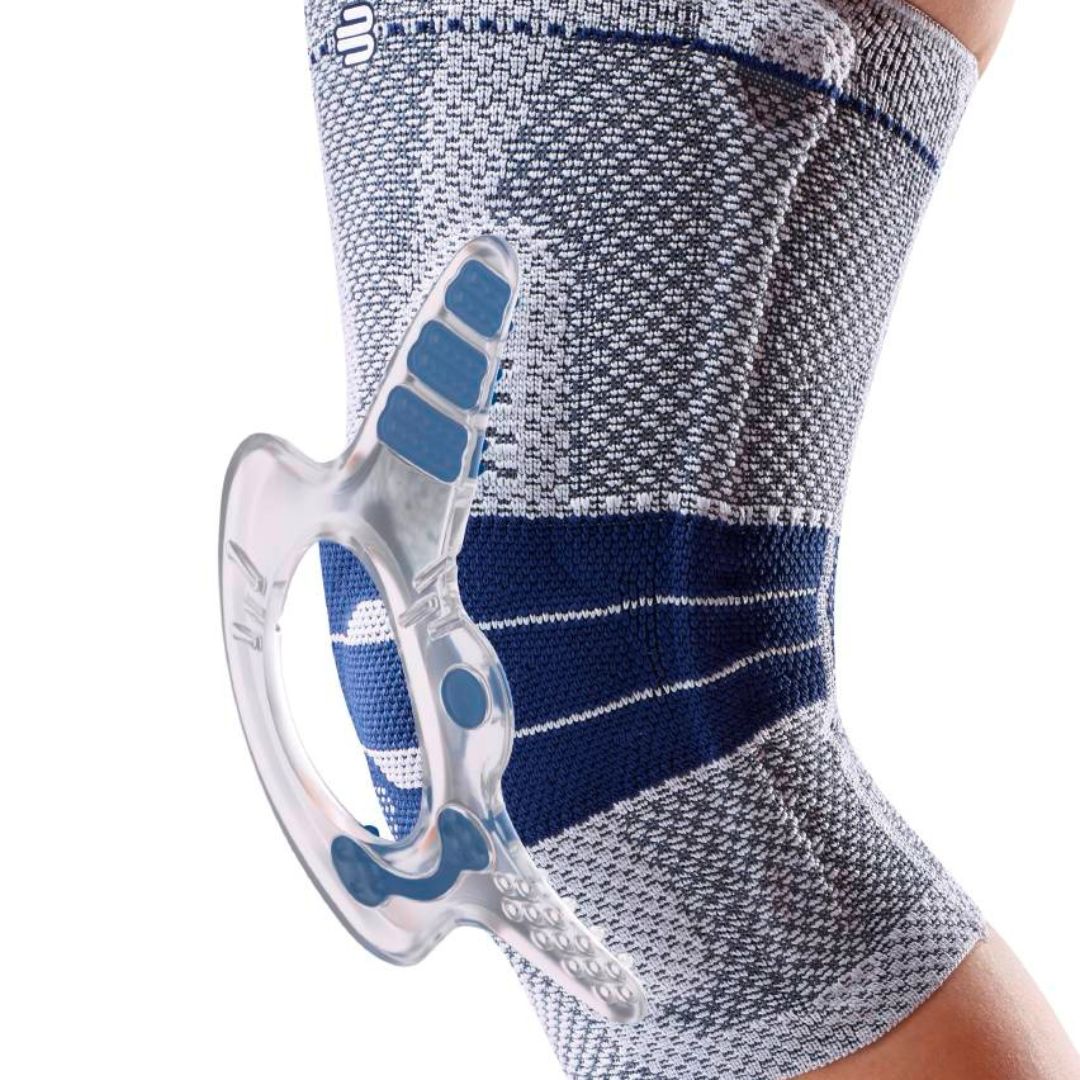
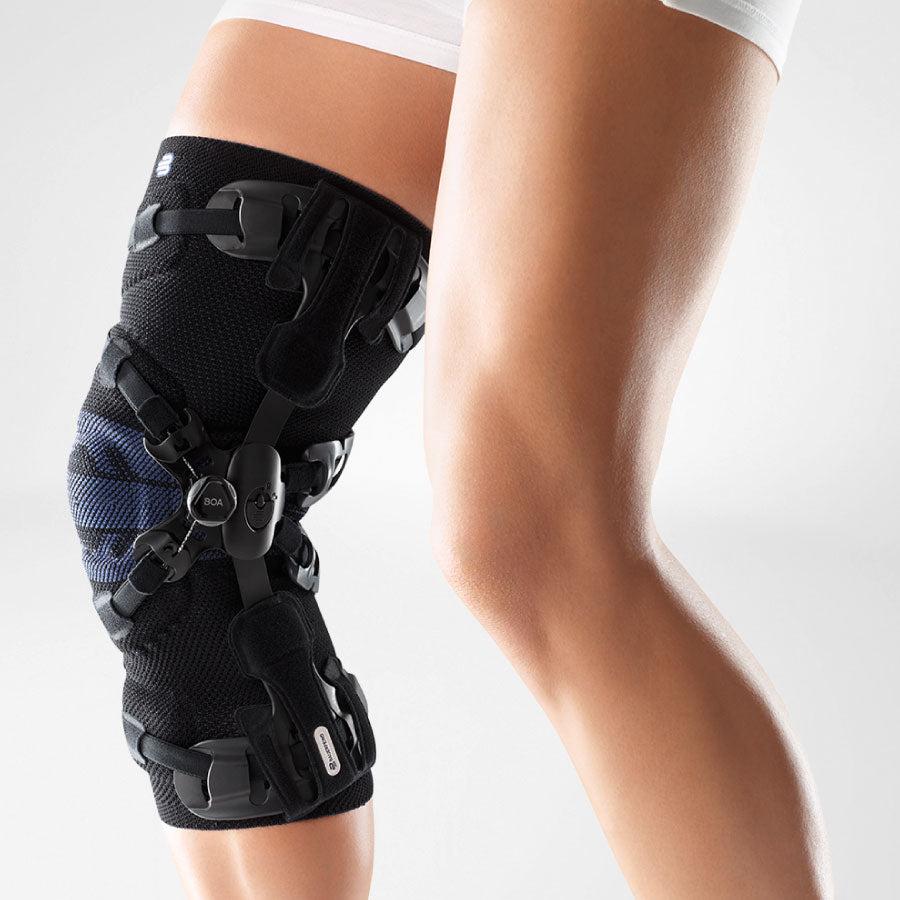
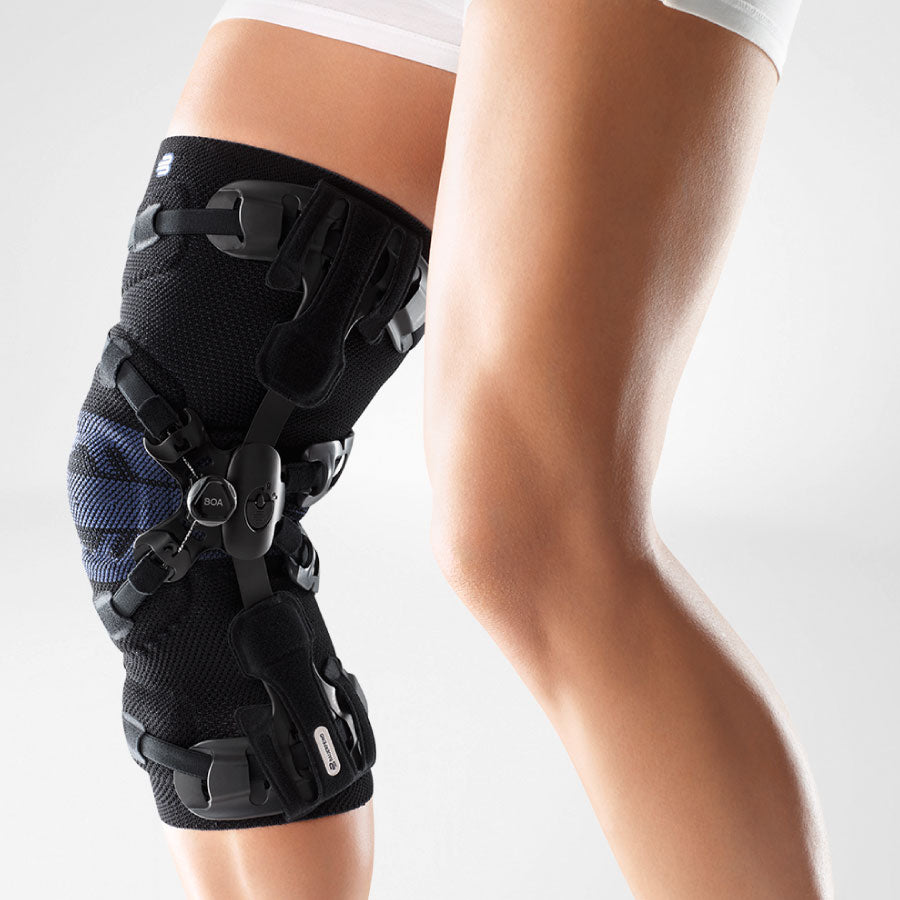
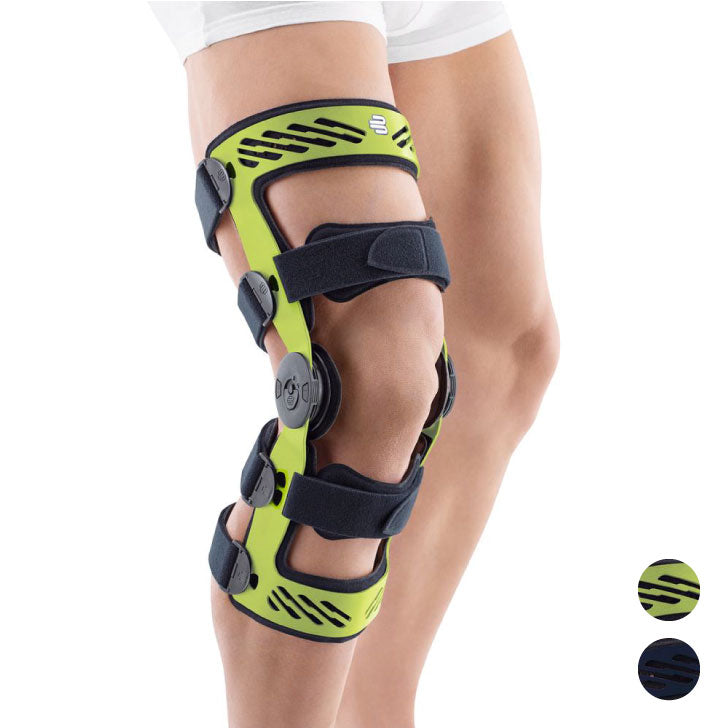
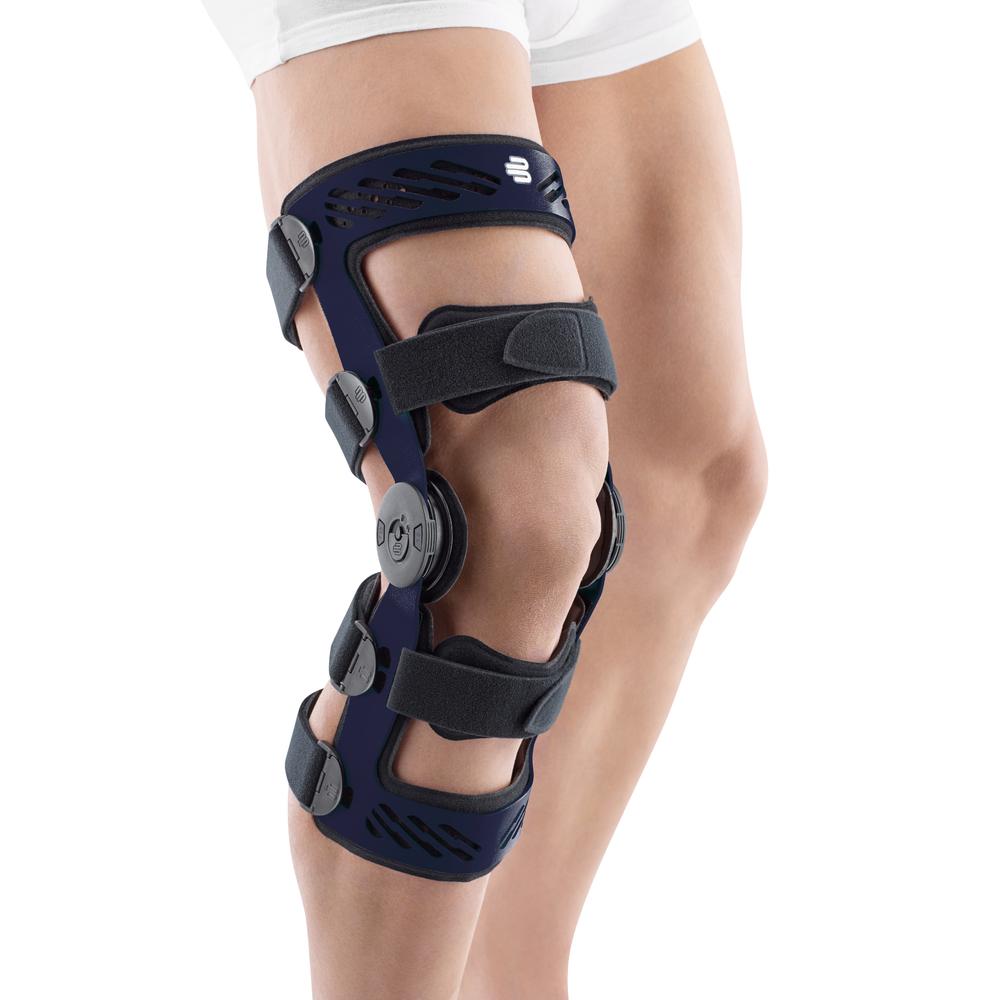
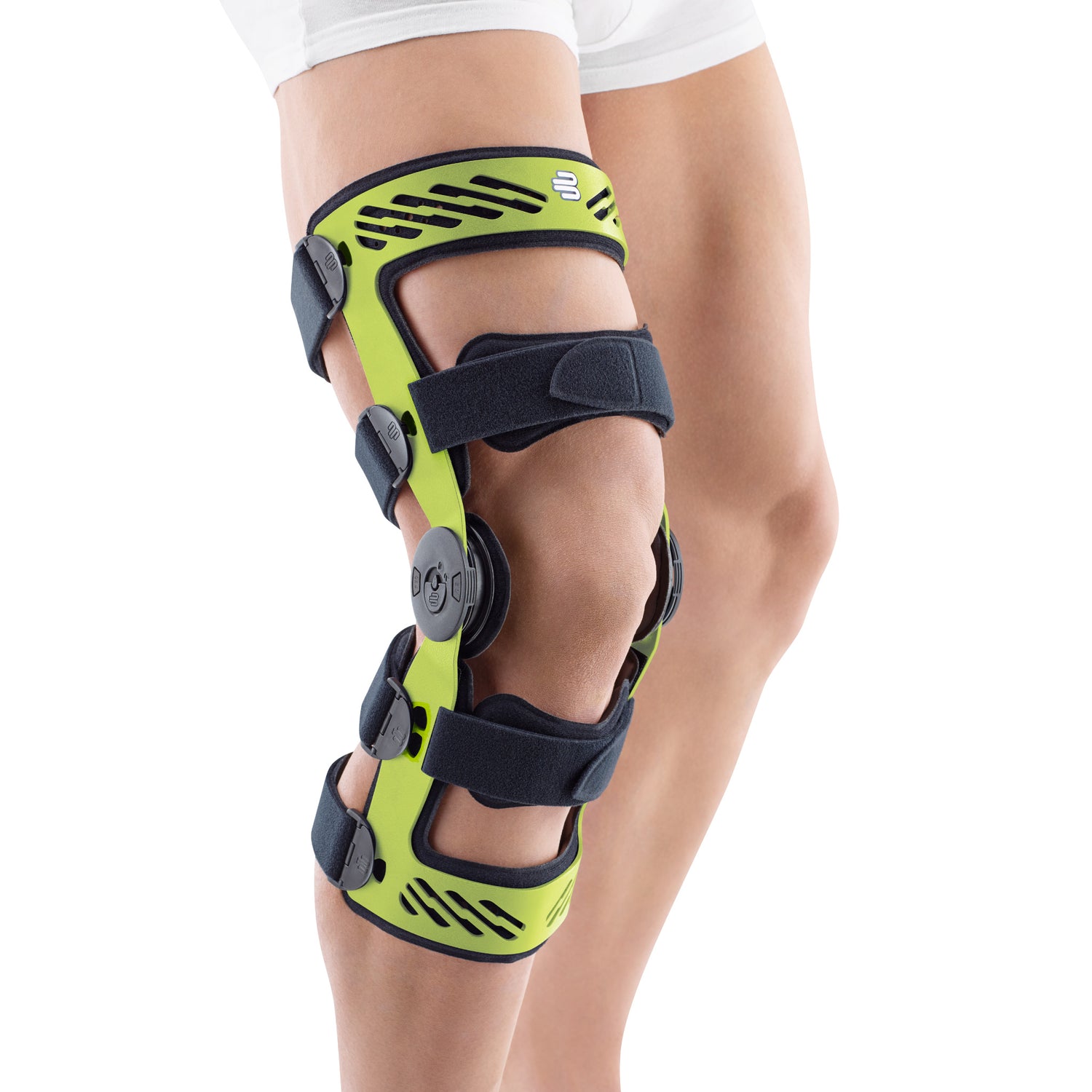
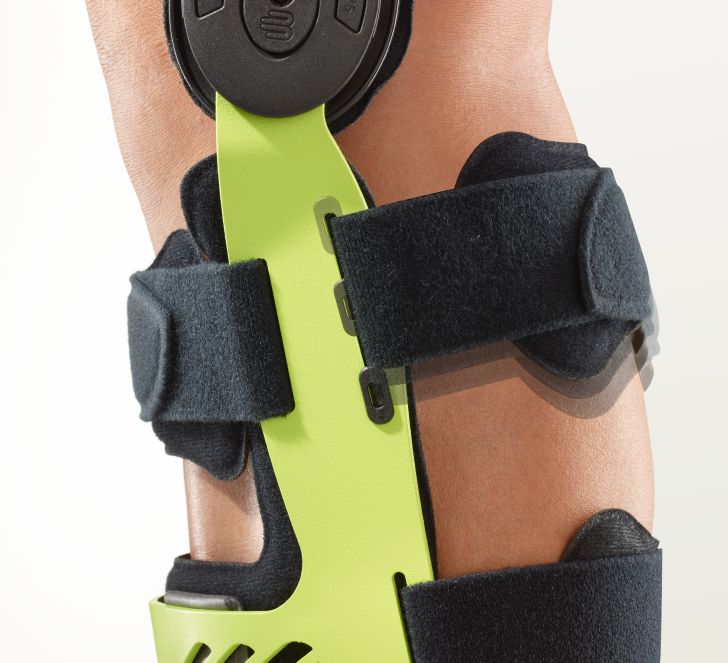
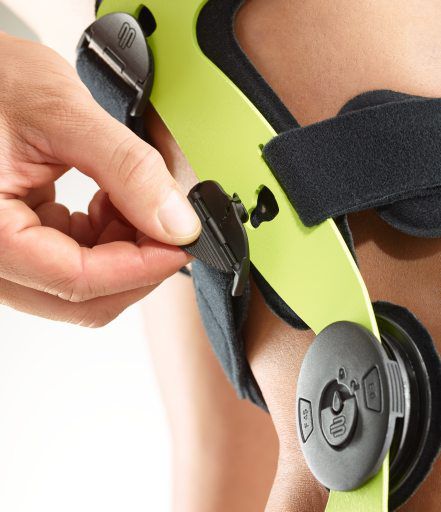
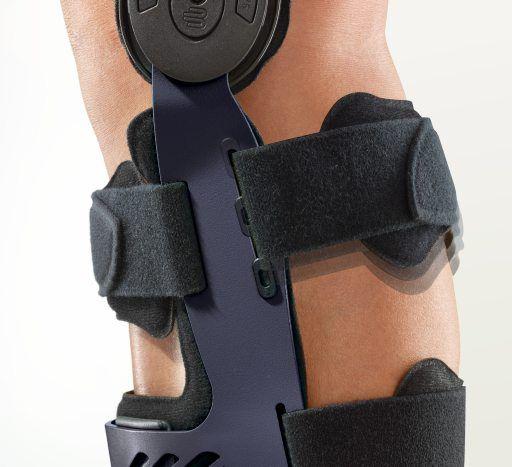
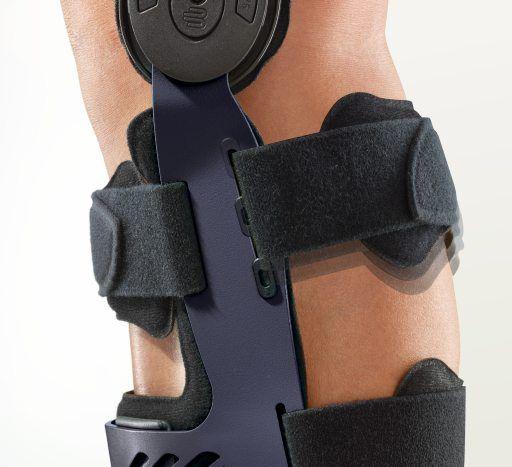
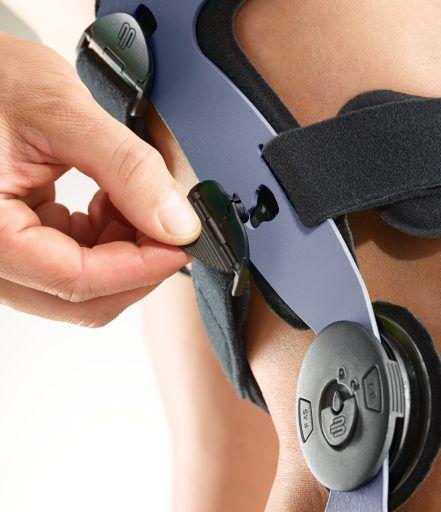
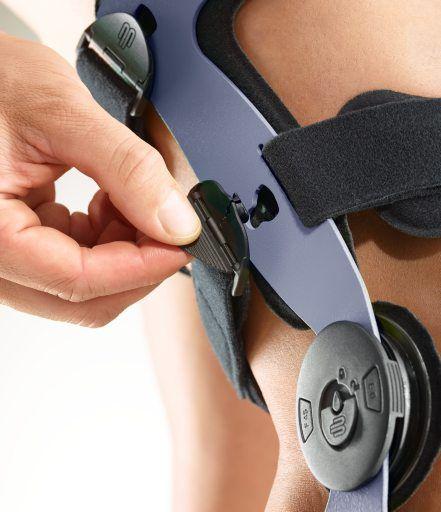
- Orthoses: Knee orthoses can help stabilize the joint and reduce pain. View orthoses
- Medication: Your doctor may prescribe painkillers, anti-inflammatory drugs, or steroid injections to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Physical therapy: A physical therapist can teach you exercises to strengthen the muscles around the knee joint and improve mobility.
- Surgical intervention: In more severe cases, surgery may be necessary to replace the damaged cartilage with an artificial joint.
Important: If you have knee pain, consult a doctor for an accurate diagnosis and an individualized treatment plan.
Note: This is only a general overview of gonarthrosis and its treatment. Each case is individual, and only a doctor can provide an accurate diagnosis and recommend the most appropriate treatment.